What Is Bile Duct Cancer?
Bile Duct
The Bile Ducts are a series of thin tubes that collect bile from the liver and gall bladder and pass it to the small intestine. Two Bile Ducts originate from the liver and one comes from the gallbladder, they join to form the common Bile Duct.
Bile Ducts collect this bile, draining it into the gallbladder and finally into the small intestine where it aids in the digestion process.
- The major function of the Bile Ducts is to move a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine.
- Bile is needed for digesting food. Its main role is to break down fats.

Bile Duct Cancer
Bile Duct Cancer also known as Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare form of cancer that arises from the cells that line the Bile Ducts . Cholangiocarcinoma occurs when cells in the Bile Ducts develop mutations in their DNA. Due to which, cells may begin to grow out of control and eventually develop into a tumor. Cholangiocarcinoma are most commonly found just outside the liver in the perihilar area. It is a slow-growing cancer that invades local structures, so the diagnosis is often delayed till the Bile Duct gets blocked. This blockade prevents bile drainage from the liver into the gallbladder and intestine. Depending upon where the blockage occurs, this can lead to inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) and/or pancreas (pancreatitis).
Types of Bile Duct Cancer
Bile Duct Cancer can start anywhere along the Bile Ducts . It is classified into different types depending on the location of origin.
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma : It develops in the smaller Bile Duct branches inside the liver. They contribute only a small number of total occurrences of Bile Duct Cancers.


Extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancers
The extrahepatic Bile Duct is made up of the hilum region and the distal region. Cancer can form in either region:
- Perihilar Bile Duct Cancer :It occurs in the hilum region. Perihilar Bile Duct Cancer is also called Klatskin tumor or perihilar cholangiocarcinoma.
- Distal extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer : These cancers are found further down the Bile Duct, closer to the small intestine.
- Multifocal Bile Duct Cancer : means that there’s more than one tumor and they’re in different sections of the bile.
Anatomy of Bile Duct Cancer
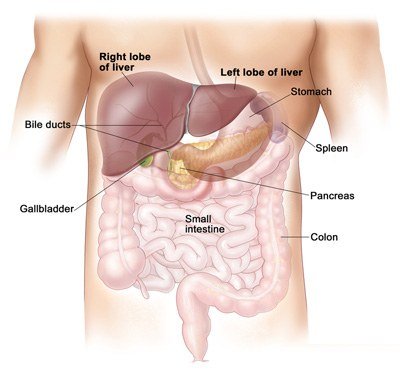
What are the general symptoms of Bile Duct Cancer?
-
Jaundice
Jaundice is often the most common symptom of Bile Duct Cancer. Jaundice occurs when the liver can’t get rid of bile, which contains a greenish-yellow chemical called bilirubin. - Light-colored/greasy stools Bilirubin contributes to the brown color of bowel movements. If the cancer blocks the release of bile and pancreatic juices into the intestine, the digestion of fatty foods becomes difficult. The undigested fat can also cause stools to be unusually pale. They might also be bulky, greasy and float in the toilet.
-
Dark urine
When bilirubin levels in the blood get high, it can also come out in the urine giving it a dark shade. -
Itching
Most people with Bile Duct Cancer notice itching caused by the excess bilirubin. -
Abdominal (belly) pain
Early Bile Duct Cancers usually do not cause pain, but more advanced cancers may cause abdominal pain, especially below the ribs on the right side. - Loss of appetite/weight loss
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
What Are The General Causes Of Bile Duct Cancer?
For most cases of Bile Duct Cancer, it is very difficult to trace the exact cause of the disease. However, there are certain factors that are known to have increased the risk. People with long-term swelling or irritation in the Bile Ducts are more likely to get this cancer. People with a bowel disease called ulcerative colitis are also at higher risk. Infection with the liver fluke parasite is also a cause of large number of Bile Duct Cancers. Some other risk factors are discussed below:
-
Chronic liver disease :
Scarring of the liver caused by a history of chronic liver disease increases the risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis that causes long-term inflammation of the liver, Biliary Stones within the Liver are some common liver troubles that end up in Cancer. -
Choledochal cyst :
It causes dilated and irregular Bile Ducts , and increases the risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma severely. -
Older age :
Cholangiocarcinoma occurs most often in adults over age 50. -
Inflammatory bowel disease :
Inflammatory bowel disease includes ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. People with these diseases have an increased risk of Bile Duct Cancer. -
Family history :
A history of Bile Duct Cancer in the family seems to increase a person’s chances of developing this cancer, but the risk is still low because this is a rare disease. -
Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins, :
including thorotrast (a special dye that used to be used in medical scans) -
Other possible risk factors :
Studies have found several other factors that might increase the risk of Bile Duct Cancer, but the links are not as clear. These include:
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Infection with HIV
- Exposure to chemicals and other radioactive chemicals
Can Bile Duct Cancer Be Prevented?
There is no proven theory to prevent Bile Duct Cancers. As with all diseases that tend to develop at an older age, living a healthy lifestyle may extend one’s lifespan. This includes not smoking, eating a balanced diet, keeping physically active, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Many of the known risk factors for Bile Duct Cancer, such as age, ethnicity, and Bile Duct abnormalities, are beyond our control. However, there are certain factors that could definitely be checked to keep the risk low. Some of them are:
- Getting vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus (HBV) to prevent infection with this virus and the cirrhosis it can cause.
- Take precautions to avoid blood-borne or sexually transmitted infections by HBV and other viruses to help prevent cirrhosis.
- Treat hepatitis infections.
- Avoid exposure to certain chemicals
What Are The Stages Of Bile Duct Cancer?
Stages of Intrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer
- Stage 0 : Abnormal cells are found in the innermost layer of tissue lining the intrahepatic Bile Duct. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue.
- Stage I : A tumor is spotted in the intrahepatic Bile Duct.
- Stage II : This stage is assigned either when a tumor has spread through the wall of the Bile Duct and into a blood vessel, or there are multiple tumors that may have spread into blood vessel.
- Stage III : The tumor has spread through the tissue that lines the abdominal wall or has spread to organs or tissues near the liver such as the duodenum, colon, and stomach.
- Stage IV :
- Stage IVA : The cancer has spread along the outside of the intrahepatic Bile Ducts or the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IVB : The cancer has spread to organs in other parts of the body.
Stages of Perihilar Bile Duct Cancer
- Stage 0 : Abnormal cells are found in the innermost layer of tissue lining the perihilar Bile Duct. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue.
- Stage I : Cancer has formed in the innermost layer of the wall of the perihilar Bile Duct and has spread into the muscle layer or fibrous tissue layer of the wall.
- Stage II : Cancer has spread through the wall of the perihilar Bile Duct to nearby fatty tissue or to the liver.
- Stage III :
- Stage IIIA : Cancer has spread to branches on one side of the hepatic artery or of the portal vein.
- Stage IIIB : Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. Cancer may have spread into the wall of the perihilar Bile Duct or through the wall to nearby fatty tissue, the liver, or to branches on one side of the hepatic artery or of the portal vein.
- Stage IV :
- Stage IVA : Cancer has spread to one or more of the following:
- main part of the portal vein and/or common hepatic artery
- branches of the portal vein and/or common hepatic artery on both sides
- right hepatic duct and the left branch of the hepatic artery or of the portal vein
- left hepatic duct and the right branch of the hepatic artery or of the portal vein.
- Cancer may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IVB : Cancer has spread to lymph nodes in more distant parts of the abdomen, or to organs in other parts of the body.
Stages of Distal extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer
- Stage 0 : Abnormal cells are found in the innermost layer of tissue lining the distalextrahepatic Bile Duct.
- Stage I :
- Stage IA : Cancer cell is found in the distal extrahepatic Bile Duct wall only.
- Stage IB : Cancer cells have spread through the wall of the distalextrahepatic Bile Duct but has not spread to nearby organs.
- Stage II :
- Stage IIA : Cancer has spread from the distal extrahepatic Bile Duct to the gallbladder, pancreas, duodenum, or other nearby organs.
- Stage IIB : Cancer has spread from the distal extrahepatic Bile Duct to nearby lymph nodes. Cancer may have spread through the wall of the duct or to nearby organs.
- Stage III : Cancer has spread to the large vessels that carry blood to the organs in the abdomen. Cancer may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV : Cancer has spread to organs in distant parts of the body.
Survival Rates Of Bile Duct Cancer?
|
Stage |
5 year Survival Rate |
|
Localized (Stage I) |
15% |
|
Regional Spread (Stage II & III) |
6% |
|
Distant Spread (Stage IV) |
2% |
|
Stage |
5 year Survival Rate |
|
Localized (Stage I) |
30% |
|
Regional Spread (Stage II & III) |
24% |
|
Distant Spread (Stage IV) |
2% |
Can Bile Duct Cancer Be Detected Early?
Bile Ducts are located deep inside the body, so early tumors can’t be felt during routine physical exams. There are no specific tests that aids in early detection of Bile Duct Cancer. Furthermore, Bile Duct Cancer does not show any early stage symptoms. Hence, most Bile Duct Cancers are found only after the cancer has grown enough to cause signs or symptoms leaving only a small number of Bile Duct Cancers cases that have been detected early.
However, if there is any reason to suspect Bile Duct Cancer, complete medical history is checked for risk factors and symptoms.
Several tests may be needed to help diagnose Bile Duct Cancer. Most common tests are:
- History and physical exam : Physical exam is conducted focusing mostly on the abdomen to check for any lumps, tenderness, or buildup of fluid. The skin and the white part of the eyes are also checked for jaundice.
- Liver function tests : Blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase released into the blood by the liver. A higher than normal amount of these substances can be a sign of liver disease that may be caused by Bile Duct Cancer.
- Laboratory tests : Several tests may be done to check samples of tissue, blood, urine, or other substances in the body.
- Blood test : is carried out to check level of bilirubin in the blood, as high level of bilirubin may indicate Bile Duct issues. Tests for albumin, liver enzymes (alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT, GGT), in the blood are also taken into account. These tests are called liver function tests. High level of these substances might point to blockage of the Bile Duct, but they can’t ascertain the reason as Cancer.
- Biopsy : where a small sample of tissue is removed so it can be looked at under a microscope for signs of Cancer
- Scans : ultrasound scan, computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
- Ultrasound : High-energy sound waves are bounced off internal tissues or organs. The echoes form a picture of body tissues called a sonogram.
- Abdominal ultrasound : This is helpful for cases with symptoms like jaundice or abdominal pain.
- Endoscopic or laparoscopic ultrasound : An ultrasound transducer is placed near the Bile Duct, to get detailed images. The transducer is either passed through the mouth, and into the small intestine near the Bile Ducts (endoscopic ultrasound) or through a small surgical cut (laparoscopic ultrasound).
- Computed tomography (CT) scan : A series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body are taken from different angles. The pictures are studied in a computer linked to an x-ray machine. CT scans can have several uses:
- Highlights the area of tumor.
- They can help stage the cancer.
- CT angiography can be used to look at the blood vessels around the Bile Ducts . This can help determine if surgery is a treatment option.
- CT scans can also be used to guide a biopsy needle into a suspected tumor or metastasis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan :
- 1. MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- 2. MR angiography (MRA)
- Cholangiography : A cholangiogram is an imaging test that looks at the Bile Ducts to see if they are blocked, narrowed, or dilated (widened). It can also be used to help plan surgery.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP): This is a non-invasive way to image the Bile Ducts .
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) : In this procedure, an endoscope is passed down the throat, through the esophagus. A small catheter is passed into the common Bile Duct. A contrast dye is injected through the tube to help outline the Bile Ducts as x-rays are taken. The images can show narrowing or blockage of these ducts.
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) : In this procedure, a thin, hollow needle is placed through the skin of the belly into a Bile Duct within the liver. A contrast dye is then injected through the needle, and x-rays are taken as it passes through the Bile Ducts . Because it is more invasive, PTC is not usually used unless ERCP has already been tried or can’t be done for some reason.
- Angiography : Angiography is an x-ray procedure for looking at blood vessels. For this test, a small amount of contrast dye is injected into an artery to outline blood vessels before x-ray images are taken. The images show if blood flow in an area is blocked or affected by a tumor, and any abnormal blood vessels in the area.
What Are The Treatments Available?
Treatment for Bile Duct Cancer depends upon where the cancer is located and whether it is possible for it to be completely removed by surgery. Unfortunately, those afflicted with this cancer tend to be older and may be unable to tolerate and recover from a major operation.
- Surgery :
- Removal of the Bile Duct : A surgical procedure to remove part of the Bile Duct if the tumor is small. Lymph nodes are removed and tissue from the lymph nodes is viewed under a microscope .
- Partial hepatectomy : The liver where cancer is found is removed.
- Whipple procedure : The head of the pancreas, the gallbladder, part of the stomach, part of the small intestine, and the Bile Duct are removed. Enough of the pancreas is left to make digestive juices and insulin.
-
Radiation therapy :
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy:
- External radiation therapy
- Internal radiation therapy
-
Chemotherapy :
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by retarding their growth. -
Photodynamic therapy :
A light-sensitive chemical is injected into a vein and accumulates in the fast-growing cancer cells. Photodynamic therapy can help relieve the signs and symptoms. -
Biliary drainage :
It is a procedure to restore the flow of bile. It can involve bypass surgery to reroute the bile around the cancer or stents to hold open a Bile Duct being collapsed by cancer. Biliary drainage helps relieve signs and symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma. -
Liver transplant :
In a liver transplant, the entire liver is removed and replaced with a healthy donated liver. A liver transplant is helpful mostly for perihilar Bile Duct Cancer.
Is There Curative Treatment For Bile Duct Cancer?
Bile Duct Cancer is mostly detected at a later stage when the cancer cell spreads and interrupts the normal functionality of the organs. Thus, making it very difficult to control and cure the cancer cells.
However, today there are several treatment options that can help control the symptoms for months or possibly years.
How Frequently Should One Visit Doctor For Early Diagnosis?
If there is any reason to suspect the occurrence of Bile Duct Cancer, consulting the doctor to get clarity is important. Also, if one is prone to the mentioned risk factors then regular blood tests and lab tests can aid in early detection of the disease thereby facilitating curative treatment.
