Liver Cancer
What Is Liver Cancer?
Liver Cancer
The Liver is the largest internal organ, weighing about 1.3 kg and is located on the right side of the belly. It is reddish-brown in color and feels rubbery when touched. Normally, we cannot feel the Liver as it is located deep inside the body and is protected by the rib cage. The Liver , gall bladder, pancreas and the intestine together process the food for digestion and absorption. Furthermore, the Liver is the most important organ for detoxification of toxins (chemicals) and for metabolism of drugs. The Liver secrets bile juice and is also responsible for the production of proteins responsible for clotting. Liver is sectioned into two large portions, the right and the left lobes.
Functions
The Liver is one of the vital organs of the body, responsible for hundreds of chemical actions necessary for life. It is also cited as a gland since it secretes digestive enzymes.
- It synthesizes multiple chemicals required by the body to function normally.
- It breaks down and detoxifies the nutrients. Some nutrients must be metabolized in the Liver before they can be used.
- It also acts as a storage unit for glycogen, iron, copper and fat-soluble vitamins (especially A, D and B12)
- The Liver generates proteins important for blood clotting that protects us from bleeding too much when there is a cut or injury.
- It secretes bile into the intestines to help absorb fats.
- It breaks down alcohol, drugs, and toxic wastes, which are then excreted in urine and stool.
Liver Cancer
Liver Cancer is a condition that happens when the normal life cycle of the cell is interrupted and instead of dying they keep growing uncontrollably and forms a tumor. This tumor may be restricted only to the Liver (benign tumor) or the Cancer cells may spread to other parts of the body (malignant tumor).
Liver Cancer is the third most frequent cause of Cancer death.
Types of Liver Cancer
Types of Benign Liver Cancers
Benign tumors are usually small, however sometimes they may grow large enough to cause problems, but they do not spread to nearby tissues or distant parts of the body. Surgery is the most preferred treatment option for such type of Cancer.
- Hemangioma : It starts in the blood vessels and is the most common type of benign Liver tumor. In most cases, no symptoms are spotted and treatment is also not essential. However, in some cases, the tumor may bleed and need to be removed surgically.
- Hepatic adenoma : Hepatic adenoma begins in the main type of Liver cell (hepatocytes). Usage of certain drugs like birth control pills or anabolic steroids may increase the risk of getting this tumor. Adenomas may shrink when the drugs are stopped. In most cases of hepatic adenoma, symptoms are not evident and treatment is also not needed. But, some of the tumors may eventually cause symptoms like pain or blood loss. Also, there is a risk that the tumor could rupture and could eventually develop into Liver Cancer; hence surgery is recommended to remove the tumor when possible.
- Focal nodular hyperplasia : Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) is a tumor-like growth made up of several cell types. Although FNH tumors are benign, it can be hard to tell them apart from true Liver Cancers, and doctors sometimes remove them when the diagnosis is unclear.
-
Types of Primary Liver Cancer
Cancer that starts in the Liver is called primary Liver Cancer. Some of the primary Liver Cancers are discussed below: - Hepatocellular Cancer : This is the most common form of Liver Cancer in adults. Malignant Cancer cells are called hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Hepatocellular Cancer (HCC) can have different growth patterns but the prognosis remains almost the same.
- It may begin as a single tumor that eventually grows larger. In later stages, it may start spreading to other parts of the Liver .
- It may start as many small Cancer nodules throughout the Liver . This is seen most often in people with cirrhosis (chronic Liver damage).
Fibrolamellar It is a rare type, making up less than 1% of HCCs. This type is most often seen in women younger than age 35, and often the rest of the Liver is not diseased. This subtype generally has a better outlook than other forms of HCC.
- Cholangiocarcinoma : Cancer that arises in the small bile ducts within the Liver is called cholangiocarcinoma. It accounts for 10 to 20 % of Liver Cancers.
-
Angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma : These are very rare, fast growing and almost incurable Cancers that begin in cells lining the blood vessels of the Liver .
Exposure to vinyl chloride or thorium dioxide increases the risk of developing these Cancers. Other factors which may be responsible for these Cancers are exposure to arsenic or radium. In about half of the cases, no likely cause is identified.
These tumors grow quickly and are usually too widespread to be removed surgically by the time they are found. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may help slow the disease, but these Cancers are usually very hard to treat. - Hepatoblastoma : This is a very rare kind of Cancer that develops in children, usually younger than 4 years old. The cells of hepatoblastoma are similar to fetal Liver cells. It can be treated successfully with surgery and chemotherapy. However, the tumors are harder to treat if they have spread outside the Liver .
Metastatic Liver Cancer
Cancer that has originated in some other part of the body and has spread to the Liver is called metastatic Liver Cancer. Liver metastases are very common in many types of Cancers, especially in case of GI tract Cancer, breast, lung and pancreas. Though, theoretically, any Cancer can spread to the Liver .
Occurrence rate
India accounts for the country with lowest Cancer incidence rates in males among all the Asian countries. Among the 9,48,858 total number of Cancer cases registered in India, 20,144 cases contributed to Liver Cancer. The mean incidence of Liver Cancer is 2.77% for males and 1.38% for females. The prevalence of Liver Cancer in India varies from 0.2% to 1.6%. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is the most prevalent etiologic factor in high incidence areas, while hepatitis C (HCV) infection is the most common in the low incidence areas
Anatomy of Liver Cancer
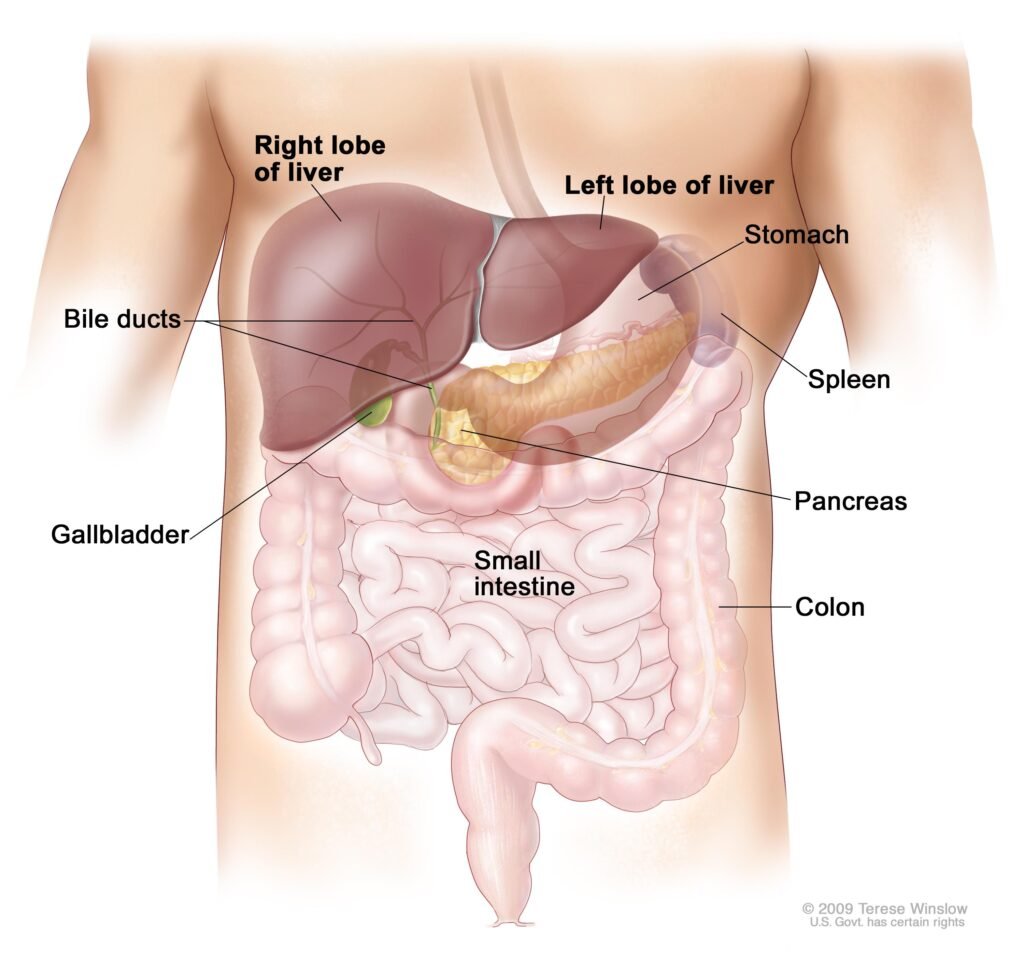
What Are The General Symptoms Of Liver Cancer?
Liver is located deep inside the body and hence usually the signs and symptoms of Liver Cancer can’t be felt until the later stages of the disease. However, in some cases it can be detected earlier. Some of the most common symptoms of Liver Cancer are:

Symptoms caused by a large size of the tumor
- Unaccounted weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Vomiting
- An enlarged Liver
- Pain and swelling in the abdomen
- Jaundice
- High blood calcium levels – hypercalcemia, that causes nausea, confusion, constipation, weakness, or muscle problems
- Low blood sugar levels – hypoglycemia, which can cause fatigue.
- Breast enlargement – gynecomastia and/or shrinkage of the testicles in men
- High counts of red blood cells – erythrocytosis which can cause someone to look red and flushed
- High cholesterol levels

Some other symptoms include fever, enlarged veins on the belly that can be seen through the skin, and abnormal bruising or bleeding. But many of the signs and symptoms of Liver Cancer can also be caused by other conditions and experiencing any of these do not ascertain Liver Cancer. Still, if any of these problems is spotted it’s important to consult a doctor right away so the cause can be found and treated if needed.
What Are The General Causes Of Liver Cancer?
There are several factors that might be responsible for the development of Cancer. Since the Liver filters blood from all parts of the body, Cancer cells from elsewhere can lodge in the Liver and start to grow. The causes of Liver Cancer may also be linked to environmental, dietary, or lifestyle factors.
A recent study involving 140 patients, hepatitis B was the most common cause of Liver Cancer affecting as many as 56 (39%) patients, followed by alcohol which affected 31 (22%) patients. T he prevalence of diabetes was found to be 25% in Liver Cancer patients.

- Anabolic steroids: These steroids are specially used by athletes and weight lifters. However, regular use can raise the risk of developing Liver Cancer considerably.
- Diabetes: People having diabetes, especially if they also have hepatitis, or regularly consume a lot of alcohol, are more likely to develop Liver Cancer.
- Family history: Any track record of the disease in the family raises an alarm.
- L-carnitine deficiency

- Smoking: Tobacco use may increase the risk of developing Adrenal Cancer.
- Arsenic: Drinking water contaminated with arsenic over a long period of time increases the risk of Liver Cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight is harmful to health. It may cause several issues including Liver Cancer.
- Smoking: This factor needs no justification. The package comes with a clear warning and reading the package gives enough information about this.
- Alcohol: While limited use of alcohol causes no harm, excess consumption is very harmful.


- Vinyl chloride and thorium dioxide (Thorotrast): Exposure to these chemicals raises the risk of angiosarcoma of the Liver . It also increases the risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular Cancer, but to a far lesser degree. Vinyl chloride is a chemical used in making plastics. Thorotrast is a chemical that in the past was injected into some patients as part of certain x-ray tests.
- Infection with parasites: Infection with the parasite that causes schistosomiasis can cause Liver damage and is linked to Liver Cancer
Can Liver Cancer Be Prevented?
Most cases of Liver Cancer could be prevented with simple lifestyle changes such as avoiding excess alcohol, having protected sex and getting vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus. A few measures to prevent Liver Cancer are:
-
Preventing hepatitis infections
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus is the most significant risk factor for Liver Cancer. These viruses can spread from person to person through contaminated needles or unprotected sex. Thus some cases of Liver Cancer may be prevented by taking care of these things. -
Limiting alcohol and tobacco use
Heavy consumption of alcohol damages the Liver thus increasing the risk of developing Liver Cancer. Limiting or avoiding alcohol may help in avoiding Liver Cancer. Smoking increases the risk of developing many Cancers including Liver Cancer, thus saying no to smoking is a smart move. -
Maintaining healthy weight
Avoiding obesity is another way to protect Liver Cancer. People who are obese are more likely to have fatty Liver disease and diabetes, both of which have been linked to Liver Cancer. -
Limiting exposure to Cancer-causing chemicals
Maintaining and implementing health and safety standards to protect consumers and workers from certain chemicals offers shielding to Liver Cancer.
What Are The Stages Of Liver Cancer?
Staging is important to understand the severity, spread and probability of cure of the disease. Once the type of Cancer is diagnosed, a stage is assigned that helps in planning the treatment for the disease.
Liver Cancer is categorized into four stages:
- Stage 1 – The spread of the tumor is limited to the Liver .
- Stage 2 – Either there are several small tumors, within the Liver , or one tumor that has reached a blood vessel
- Stage 3 – either there are various large tumors, or there is just one that has reached the main blood vessel(s). Cancer may have also reached the gallbladder
- Stage 4 – The Liver Cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Survival Rates Of Liver Cancer?
Survival rate of Liver Cancer is determined by analyzing and studying the cases of patient’s having the same disease at the same stage. However, these rates cannot predict precisely the probability of cure or survival of any patient, as each patient is unique and their survival depends on a lot of other factors like immunity, response to treatment, health record etc. These statistics of survival rate is just a reference to understand the severity and criticality of the disease. Below are some details on the survival rate for 5 years:
| Stage | 5 year Survival Rate |
| Localized | 31%. |
| Regional | 11%. |
| Distant | 3%. |
Due to the asymptomatic nature of these infections, about 60% of infected individuals remain unaware until they show symptoms of cirrhosis or Liver Cancer which may take over 20 years. Both cirrhosis and Liver Cancer are irreversible and cause death.
Can Liver Cancer Be Detected Early?
It is often hard to find Liver Cancer early because signs and symptoms often do not appear until it is in its later stages. Small Liver tumors are hard to detect on a physical exam because most of the Liver is covered by the right rib cage. By the time a tumor can be felt, it might already be quite large.
For people at higher risk of Liver Cancer due to cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B infection, some experts recommend screening for Liver Cancer with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood tests and ultrasound exams every 6 to 12 months. Ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures of internal organs.
Once a suspicion of Liver Cancer arises, a physician will order one the following to confirm a diagnosis:
- Blood tests: Alfa-fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein present in the blood, whose presence may be elevated in patients with Liver Cancer. But looking at AFP levels isn’t a perfect test for Liver Cancer. Many patients with early Liver Cancer have normal AFP levels. Also, AFP levels can be increased from other kinds of Cancer as well as some non-Cancerous Liver conditions.
- Imaging studies: The best way to detect Liver Cancer is through surveillance ultrasound of the Liver done every 6 months in a patient with a diagnosis of cirrhosis. As with most forms of Cancer, it is best to treat the Liver Cancer as soon as it is detected.
- Liver biopsy is performed to by extracting sample tissues from the Liver , which are then analyzed under a microscope to look for Cancer cells. But Liver biopsy is not the most preferred option as it carries several risks like infection, bleeding, or seeding of the needle. Seeding is when Cancer cells get on the needle used for a biopsy and spread to other areas touched by the needle. Liver biopsy of suspected Liver Cancer carries the added risk of seeding the Liver biopsy needle track in 1% to 3% of cases.
- HCC screeningx – high risk individuals for HCC should have regular screenings for Liver Cancer. Liver Cancer, if not diagnosed early is much more difficult to remove. The only way to know whether you have Liver Cancer early on is through screening because symptoms are either slight or non-existent.
What Are The Treatments Available?
The medical treatment chosen depends on how much Cancer has spread and the general health of the Liver .

Surgery is one of the most common treatment options if the Cancer is small and is limited to some part of the Liver .

In this procedure, the Cancerous Liver of the patient is removed and is replaced with a healthy Liver from another person. It is usually used in cases where the Cancer cells are unresectable.

In this procedure the Cancer cells in the Liver are killed without any surgery. Heat, laser, or injecting a special alcohol or acid directly into the Cancer are used to kill the Cancer cells. This technique may be used in palliative care when Cancer is unresectable.

Blocking the blood supply to Cancer can be done using a procedure called embolization. This technique uses a catheter to inject particles or beads that can block blood vessels that feed Cancer. Starving the Cancer of the blood supply prevents the growth of the Cancer. This technique is usually used on patients with large Liver Cancer for palliation.

Radiation uses high-energy rays directed to the Cancer to kill Cancer cells. Normal Liver cells are also very sensitive to radiation. Complications of radiation therapy include skin irritation near the treatment site, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting.

Chemotherapy is a technique that kills Cancer cells by the use of drugs given either orally or by injections. Complications of chemotherapy include fatigue, easy bruising, hair loss, nausea and vomiting, swollen legs, diarrhea, and mouth sores. These side effects are usually temporary.

Sorafenib (Nexavar) is an oral medication that can prolong survival (up to 3 months) in patients with advanced Liver Cancer. Side effects include fatigue, rash, high blood pressure, sores on the hands and feet, and loss of appetite

A complete curable treatment of Liver Cancer is quite difficult. Also, in most of the cases of Liver Cancer, the detection is delayed till later stages, where Cancer has spread to different organs. While Liver Cancer is usually difficult to cure, treatment consists of chemotherapy and radiation. In some cases, surgical resection or Liver transplantation is performed.
01

People with a high risk of Liver Cancer are recommended to visit the doctor in every 6 months for regular screening tests that might help in the early detection of this silent disease.
02

Being aware of the symptoms, and any health issue that might indicate the presence of the disease needs to be examined thoroughly. Also, going for screening tests might unveil the presence of the disease in an early stage thus making treatment easier.
