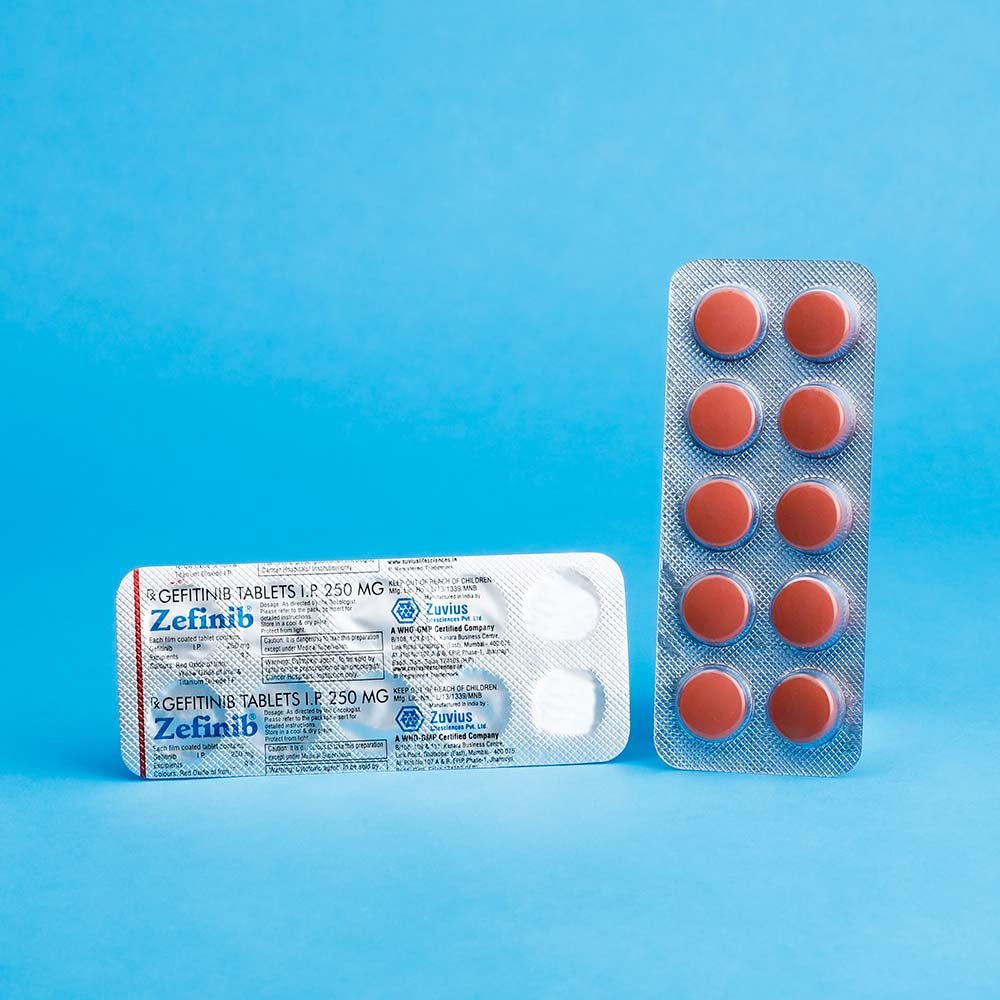
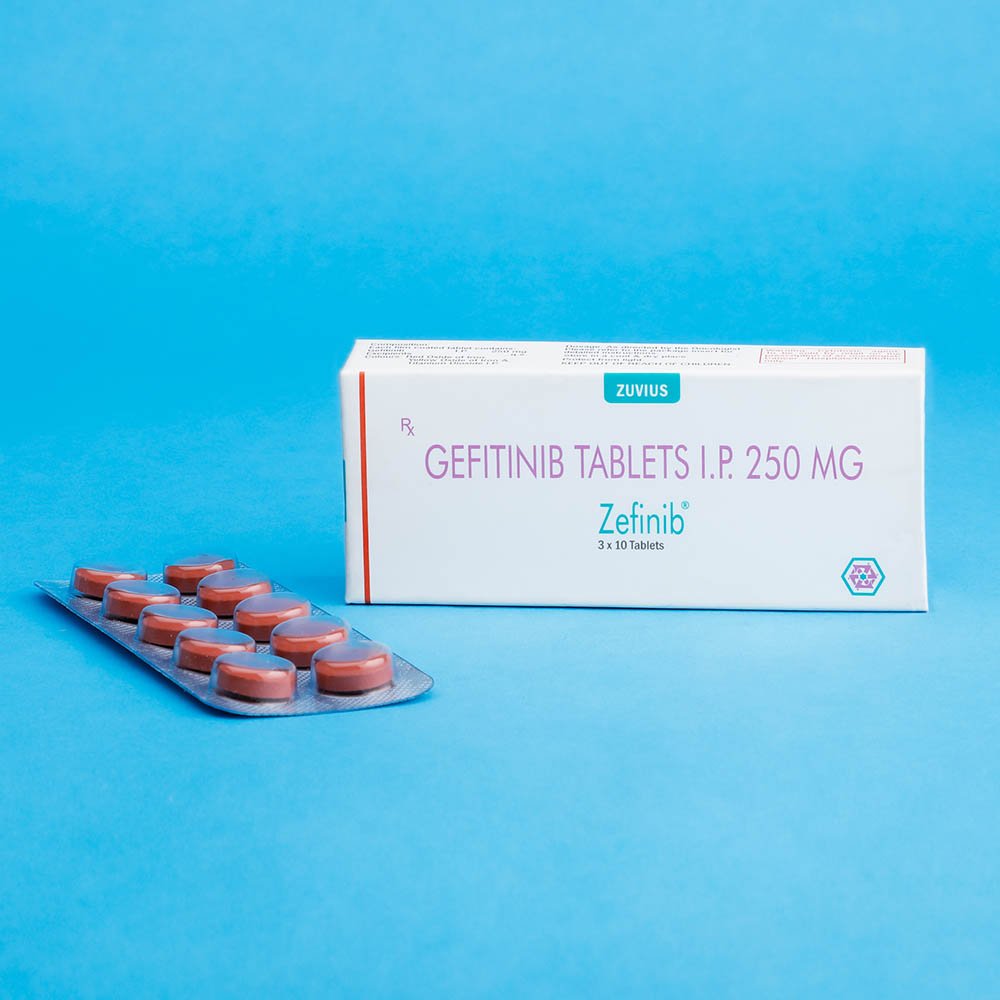
Zefinib Tab- Gefitinib Tab 250 mg
Gefitinib Tab
Strength: 250mg
Pack Size: 1 x 10
Drug Class: antineoplastic agents, protein kinase inhibitors
Dosage and Administration:
Patient Selection
Select patients for the first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC with IRESSA based on the presence of EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutations in their tumor or plasma specimens [see INDICATIONS AND USAGE, Clinical Studies]. If these mutations are not detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue if feasible.
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of EGFR mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dose
The recommended dose of IRESSA is 250 mg orally once daily with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Do not take a missed dose within 12 hours of the next dose.
Administration To Patients Who Have Difficulty Swallowing Solids
Immerse IRESSA tablets in 4 to 8 ounces of water by dropping the tablet in water, and stir for approximately 15 minutes. Immediately drink the liquid or administer through a naso-gastric tube. Rinse the container with 4 to 8 ounces of water and immediately drink or administer through the naso-gastric tube.
Cold Storage: no
Gefitinib is a kinase inhibitor.
The chemical name of gefitinib is 4-Quinazolinamine N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] and the following structural formula:
 |
Gefitinib has the molecular formula C22H24ClFN4O3, a relative molecular mass of 446.9 daltons and is a white-colored powder. Gefitinib is a free base. The molecule has pKas of 5.4 and 7.2. Gefitinib can be defined as sparingly soluble at pH 1, but is practically insoluble above pH 7, with the solubility decreasing sharply between pH 4 and pH 6. In non-aqueous solvents, gefitinib is freely soluble in glacial acetic acid and dimethyl sulfoxide, soluble in pyridine, sparingly soluble in tetrahydrofuran, and slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol (99.5%), ethyl acetate, propan-2-ol and acetonitrile.
IRESSA® (gefitinib) tablets are available as brown film-coated tablets, containing 250 mg of gefitinib, for oral administration. The inactive ingredients of the tablet core of IRESSA tablets are lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate and magnesium stearate. The tablet coating is composed of hypromellose, polyethylene glycol 300, titanium dioxide, red ferric oxide and yellow ferric oxide.
Gefitinib is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of patients with locally advanced of metastatic non small cell lung cancer after failure of both platinum based and docetaxel chemotherapies. The effectiveness of Gefitinib is based on objective response rates. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit. such as improvement in disease-related symptoms or increased survival. Results from two large, controlled, randomized trials in first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer showed no benefit from adding Gefitinib to doublet, platinum based chemotherapy. Therefore, Gefitinib is not indicated for use in this setting.
Usage-:
Gefitinib is used to treat metastatic (cancer that has already spread) non-small cell lung cancer in patients who have certain types of abnormal epidermal growth factor (EGFR) genes, and did not receive cancer medicines in the past. Your doctor will perform a test before you take this medicine
In preclinical testing, oral gefitinib inhibited the growth of NSCLC tumors that express the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a mediator of cell signaling, and phase 1 trials have demonstrated that a fraction of patients with NSCLC progressing after chemotherapy experience both a decrease in lung cancer
Read the label carefully before use
keep out of the reach of children
Protect from Light
Hepatotoxicity : Asymptomatic increases in liver transaminases have been observed in Gefitinib treated patients. therefore,periodic liver function (transaminases, bilarubin, and alkaline phosphate) testing should be considered.Discontinuation Gefitinib should be considered if changes are severe. Patients with Hepatic Impairment In vitro and in vivo evidence suggest that Gefitinib is cleared primarily by the liver. Therefore, Gefitinib exposure may be increased in patients with hepatic dysfunction. In patients with liver metastases and and moderately to severely elevatedbiochemical liver abnormalities, however, Gefitinib pharmacokinetics were similar to the pharmacokinetics of individuals without liver abnomalities. The influence of non-cancer related hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Gefitinib has not been evaluated.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fetility
Gefinib has been tested for genotoxicity in a series of in vitro (bacterial mutation, mouse lymphoma and human lymphocyte) assays and an in vivo micronueus test. Under the conditions of these assays. Gefitinib did not cause genetic damage.
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with Gefitinib.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
Nursing Mothers :
It is know whether Gefitinib is excreted in human milk. Following oral administration of carbon – 14 labeled Gefitinib to rats 14 days postpartum, concentrations of radioactivity in milk were higher than in blood. Levels of Gefitinib and its metabolities were 11- to – 19 – fold higher in milk than in blood, after oral exposure of lactating rats to a dose of 5 mg/kg. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women should be advised against breast-feeding while receiving Gefitinib therapy
Pediatric Use :
Gefitinib is not indicated for use in pediatric patients as safety and effectiveness have not been established. In clinical trials of Gefitinib alone or with radiation in pediatric patients with primary central Nervous System (CNS) tumors, cases of CNS hemorrhage and death have been reported. There is insufficient data inpediatric patients to establish a causal relationship. There is no evidence to suggest increased risk of cerebal hemorrhage in adult patients with NSCLC receiving Gefitinib.
Geriatric Use :
Of the total number of patients participating in trials of second and third line Gefitinib treatment of NSCLC, 65% were aged 64 years or less, 30.5% were aged 65 to 74 years, and 5% of patients were aged 75 years or older. No differences in safetyor efficacy were observed between younger and older patients.
Patients with Several Renal Impairment :
The effect of several renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Gefitinib is not known. Patients with severe renal impairment should be treated with caution when given Gefitinib.