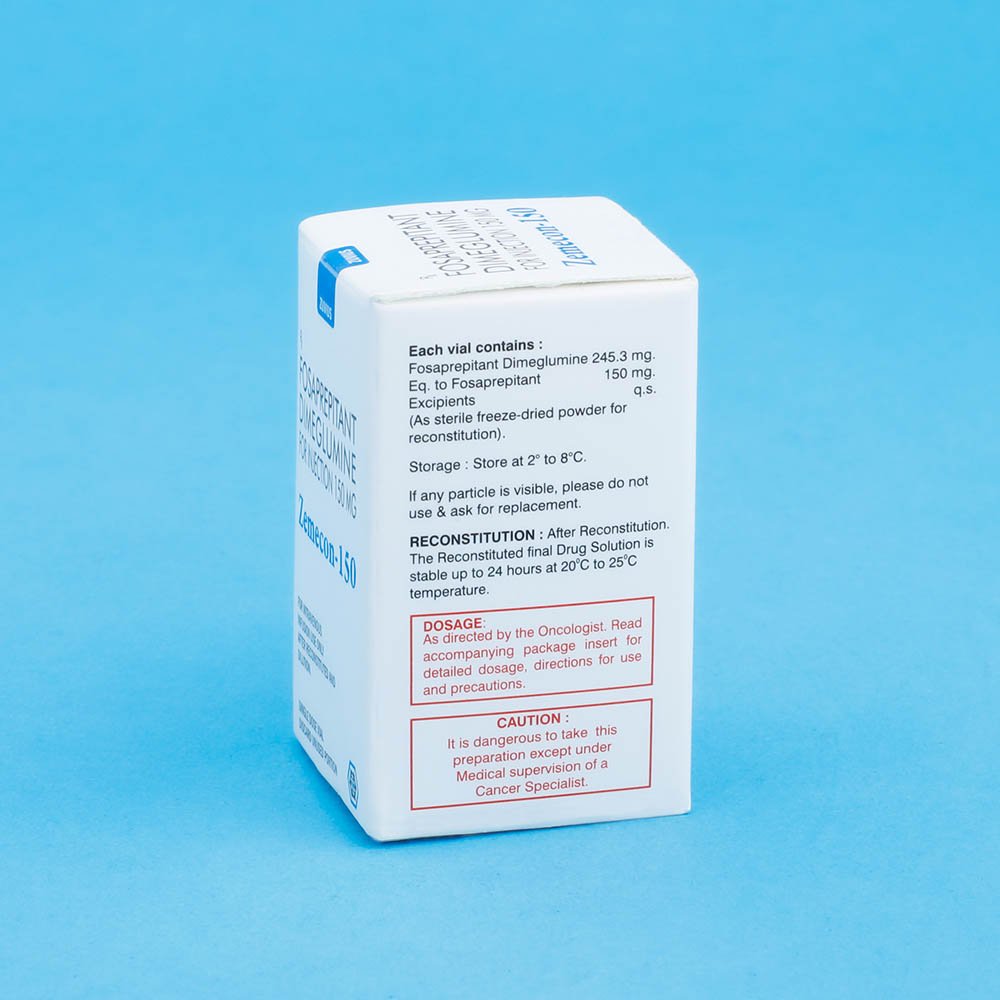
Zemecon- Fosaprepitant Inj 150 mg
Fosaprepitant
Strength: 150mg
Pack Size: 1 vial
Drug Class: Antiemetic Agents
Dosage and Administration:
Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy(HEC)
Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg (Single Dose Regimen of Fosaprepitant):
Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg is administered intravenously on Day 1 only as an infusion over 20.30 minutes initiated approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy. No capsules of Fosaprepitant are administered on Days 2 and 3. Fosaprepitant for Injection should be administered in conjunction with a corticosteroid and a 5-HT3 antagonist as specified in Table 1. The recommended dosage of dexamethasone with Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg differs from the recommended dosage of dexamethasone with Fosaprepitant for Injection 115 mg on Days 3 and 4.
Table 1: Recommended dosing (3-Day Dosing Regimen of Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg) for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | |
| Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg | 150 mg intravenous | none | none | none |
| Dexamethasone** | 12 mg orally | 8 mg orally | 8 mg orally twice daily | 8 mg orally twice daily |
| Ondansetron | 32 mg intravenous | none | none | none |
Dexamethasone should be administered 30 minutes prio to chemotherapy treatment on Day 1 and in the morning on Days 2 through 4. The dose of dexamethasone accounts for drug interactions.
Ondansetron should be administered 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy treatment on Day
Preparation of Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg
Table 2: Preparation Instructions for Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg
| Step 1 | Aseptically withdraw 5 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride for injection IP from 500 mL infusion bag. Aseptically inject 5 mL 0.9% Sodium Chloride for Injection IP (normal saline) into the vial. Assure that normal saline is added to the vial along the vial wall in order to prevent foaming. Swirl the vial gently. Avoid shaking and jetting saline into the vial. |
| Step 2 | Aseptically prepare an infusion bag filled with 145 mL of normal saline . |
| Step 3 | Aseptically withdraw the entire volume from the vial and transfer it into the infusion bag containing 145 mL of normal saline to yield a total volume of 150 mL and a final concentration of 1 mg/1 mL. |
| Step 4 | Gently invert the bag 2-3 times. |
The reconstituted final drug solution is stable for 24 hours at ambient room temperature (at or below 25°C).
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration whenever solution and container permit.
Cold Storage: yes
Fosaprepitant dimeglumine for Injection is a sterile, lyophilized prodrug of aprepitant, a substance P/neurokin in-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, and is chemically described as 1- Deoxy-1- (methylamino)-D-glucitol[3-[[(2R,3S)-2-[(1R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyllethoxy]-3-(4- fluorophenyl)-4-morpholinyl]methyl]-2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl] phosphonate(2:1) (salt). Its empirical formula is C23H22F7N4O6P. 2(C7H17NO5)and its structural formula is:
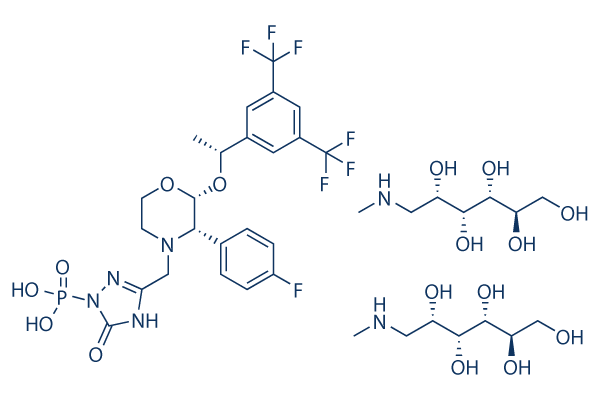
Fosaprepitant dimeglumine is a white to off-white amorphous powder with a molecular weight of 1004.83. It is freely soluble in water. Each vial of Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg for intravenous administration contains 245.3 mg of fosaprepitant dimeglumine equivalent to 150 mg of fosaprepitant free acid and the following inactive ingredients: edetate disodium (18.8 mg), polysorbate 80 (75 mg), lactose anhydrous (375 mg), sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment). Fosaprepitant dimeglumine hereafter will be referred to as fosaprepitant.
Fosaprepitant for Injection is a substance P/neurokinin-1 (NK,) receptor antagonist indicated in adults for use in combination with other antiemetic agents for the:
- prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (HEC) including high-dose cisplatin.
- prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (MEC).
Fosaprepitant (4.0 mg/kg) in addition to ondansetron, without application of dexamethasone, was well tolerated, safe, effective and superior to ondansetron only as CINV prophylaxis in pediatric patients during moderately and highly emetogenic chemotherapy.
- CYP3A4 InteractionsFosaprepitant is rapidly converted to aprepitant, which is a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4 when administered as a 3-day antiemetic dosing regimen for CINV. Fosaprepitant should be used with caution in patients receiving concomitant medications that are primarily metabolized through CYP3A4. Inhibition of CYP3A4 by aprepitant or fosaprepitant could result in elevated plasma concentrations of these concomitant medications. When fosaprepitant is used concomitantly with another CYP3A4 inhibitor, aprepitant plasma concentrations could be elevated. When aprepitant is used concomitantly with medications that induce CYP3A4 activity,aprepitant plasma concentrations could be reduced, and this may result in decreased efficacy of aprepitant. Chemotherapy agents that are known to be metabolized by CYP3A4 include docetaxel, paclitaxel, etoposide, irinotecan, ifosfamide, imatinib, vinorelbine, vinblastine and vincristine. In clinical studies, the oral aprepitant regimen was administered commonly with etoposide, vinorelbine, or paclitaxel. The doses of these agents were not adjusted to account for potential drug interactions. In separate pharmacokinetic studies, no clinically significant change in docetaxel or vinorelbine pharrnacokinetics was observed when the oral aprepitant regimen was coadministered.Due to the small number of patients in clinical studies who received the CYP3A4 substrates vinblastine,vincristine,or ifosfamide,particular caution and careful monitoring are advised in patients receiving these agents or other chemotherapy agents metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 that were not studied
This medicine may cause infusion-related reactions, which can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Tell your doctor right away if you start to have a fever, chills or shaking, dizziness, trouble breathing, itching or rash, lightheadedness or fainting after receiving this medicine.