Lung Cancer
What Is Lung Cancer?
Lungs
The lungs are a pair of large, spongy, air-filled respiratory organs located on either side of the chest (thorax). They are specialized for gas exchange between our blood and the air. The lungs are covered by a thin layer of tissue called the pleura. A thin layer of fluid acts as a lubricant allowing the lungs to slip smoothly as they expand and contract with each breath.
The lungs expand and contract up to 20 times a minute to supply oxygen all over the body and expel carbon dioxide that has been generated throughout the body.
- The right lung has three lobes called upper, middle and lower lobes.
- The left lung has only two lobes, the upper and lower lobe.
Functions of Lungs

- Maintaining the pH of blood by maintaining the amount of Carbon dioxide in the body.
- Air is warmed, humidified, and cleaned by the nose and lungs.
- Filtering out small gas bubbles that may occur in the bloodstream.
- Converting a chemical in the blood called angiotensin I to angiotensin II. These chemicals are important for controlling blood pressure.
- The medulla secretes stress hormones that generate the primitive stress response.
Lung Cancer
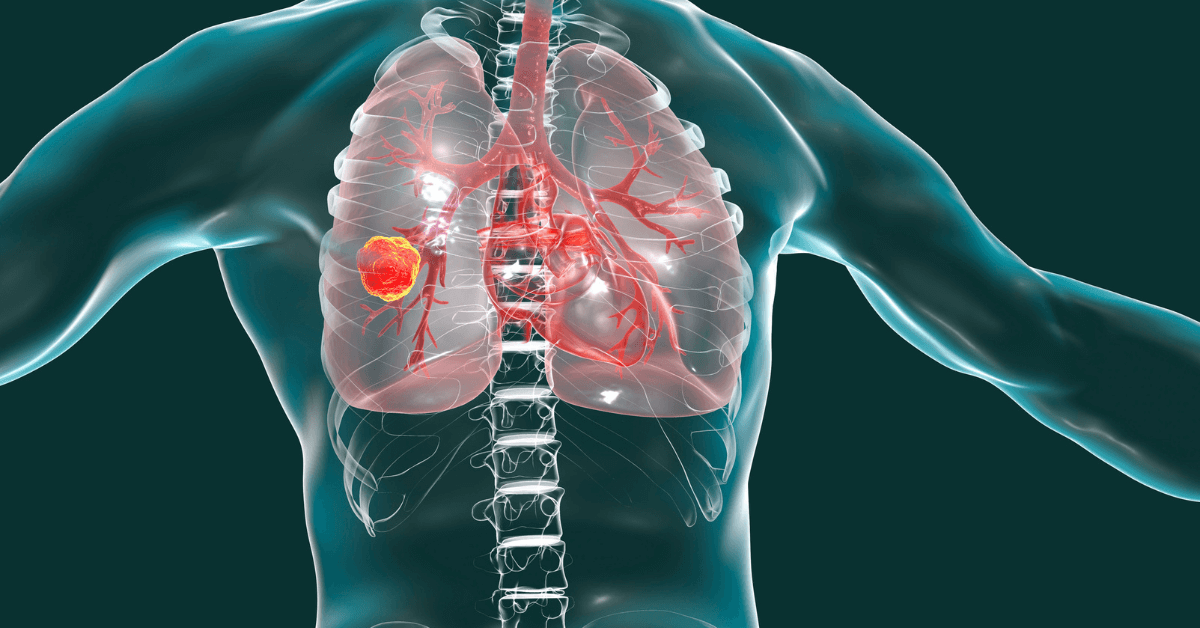
Cancer is the uncontrollable growth of abnormal cells that may lead to the formation of a lump or tumor. Cancer starts when any change in the gene forces the cell to grow and multiply uncontrollably. Thus resulting in the growth of a hard mass called tumour. When the cells in the lungs start behaving in an unaccounted manner and continue to grow without dying then it is termed as primary lung cancer. As tumors become larger and more numerous, they undermine the lung’s ability to provide the bloodstream with oxygen.
These tumors may be either benign or malignant. Benign tumors (non cancerous) are comparatively less destructive and cannot spread from its primary location. Malignant tumour is a group of cancer cells that can invade and destroy nearby tissue. They are more dangerous and spread to other parts of the body either through the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. Metastasis refers to cancer spreading beyond its site of origin to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads it is much harder to treat successfully.
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer is divided into non-small cell Lung Cancer and small cell Lung Cancer based on the type of cells that is mutated. Non-small cell Lung Cancer is much more common than small cell Lung Cancer.

Non–small cell Lung Cancer
Also known as adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, they account for 80% of Lung Cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma usually starts in glandular cells on the outer part of the lung. They can also start in flat, thin cells called squamous cells. These cells line the bronchi, which are the large airways that branch off from the windpipe (trachea) into the lungs. There are four different types of non–small cell Lung Cancer and each of them have different treatment options:

Squamous cell carcinoma
This is the most common type Lung Cancer in men. This cancer forms in the lining of the bronchial tubes.

Adenocarcinoma
This is the most common type of Lung Cancer in women and in non smokers, adenocarcinoma forms in the mucus-producing glands of the lungs.

Bronchioalveolar carcinoma
This is a rare type of adenocarcinoma that forms near the lungs’ air sacs.

Large-cell undifferentiated carcinoma
A rapidly growing cancer, large-cell undifferentiated carcinomas form near the outer edges or surface of the lungs.

Small cell Lung Cancer
These cancers usually start in cells that line the bronchi in the centre of the lungs. The main types of small cell Lung Cancer are small cell carcinoma and combined small cell carcinoma. Small cell Lung Cancer accounts for 20% of Lung Cancer cases and is mostly caused due to smoking.
Anatomy Of Lung Cancer

Occurrence Rate of Lung Cancer
According to National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) reports, Lung Cancer is the second most common cancer and the most common cause of cancer related deaths all over the world. It accounts for 13% of all new cancer cases and 19% of cancer related deaths worldwide. In India, Lung Cancer constitutes 6.9% of all new cancer cases and 9.3% of all cancer related deaths in both sexes. The highest reported incidences of Lung Cancer are from Mizoram in both males and females. The time trends of Lung Cancer show a significant rise in Delhi, Chennai and Bangalore in both sexes.
What Are The Symptoms Of Lung Cancer?
Unfortunately, there are no prominent symptoms of early Lung Cancers. For about 25% of people with Lung Cancer, symptoms are not diagnosed even after having a chest X-ray or CT during a routine test or as a procedure for other problems. Lung Cancer symptoms that may be detected are listed below.
- Persistent Cough that may sound a bit different or be painful. Coughing up phlegm that contains blood also indicates something serious.
- Fatigue or breathlessness or wheezing
- Loss of appetite and unaccounted weight loss are also signaling something that needs your attention.
- Chest pain or pain in the shoulder. It could be a dull ache or a sharper pain.
- Ongoing chest infections which may occur often or doesn’t get better with treatment.
- Some types of Lung Cancer cells produce Ectopic hormones that go into the bloodstream. These hormones can cause symptoms that don’t seem related to the Lung Cancer. These symptoms are also called paraneoplastic syndrome. Some of the hormone symptoms are:
- pins and needles or numbness in the fingers or toes
- muscle weakness
- drowsiness, weakness, dizziness and confusion
- breast swelling in men
- blood clots
What Are The General Causes Of Lung Cancer?
Lung Cancer occurs when a lung cell’s gene mutation damages the cell’s DNA. Mutations can occur for a variety of reasons. The exact cause of Lung Cancer is still being investigated. However, certain risk factors have been identified to play a major role in causing cells to become cancerous.
- Inhaling of carcinogenic substances is the major cause of Lung Cancer. Tobacco, asbestos, arsenic, radiation such as gamma and x-rays, the sun, and compounds in car exhaust fumes are all examples of carcinogens. These substances are directly responsible for damaging DNA and aiding cancer.
- Smoking: About 87% of Lung Cancers are related to smoking. According to an article published in newscientist.com, theverge.com one genetic mutation is induced in every 50 cigarettes smoked. Even exposure to second-hand smoke can damage cells and result in cancer. Radon gas, pollution, toxins, and other factors contribute to the remaining 10%.
- Lead (a highly poisonous metal)
- Arsenic (an insecticide)
- Cadmium (a battery component)
- Isoprene (used to make synthetic rubber)
- Benzene (a gasoline additive)
- Indoor radon exposure is now the second most common cause of Lung Cancer.
- Genes: Genetic predisposition that is inherited from family members is also a known cause of Lung Cancer. A child may be born with certain genetic mutations that make him/her more likely to develop cancer later in life. Genetic predispositions are thought to either directly cause Lung Cancer or greatly increase one’s chances of developing Lung Cancer from exposure to certain environmental factors.
- Occupational and environmental carcinogens
- Asbestos
- Arsenic
- Plycyclic Hydrocarbon
Cigarette smoke damages and can kill hair-like projections called cilia. The cilia normally sweep out toxins, carcinogens, viruses, and bacteria. As the cilia get destroyed by continuous smoke, it fails to perform its functions thus allowing items to accumulate in the lungs that may lead to troubles like lung infections or Lung Cancer.

is the most important measure that can prevent the development of Lung Cancer. About 90% of the cases of Lung Cancer are attributed to smoking and inhaling of carcinogenic substances so avoiding these factors definitely lowers the risk of getting cancer. For smokers who quit within 10 years the risk of getting Lung Cancer drops to about the same risk as if they had never smoked.
01

Even continual inhalation of the air contaminated with smoke increases the risk of getting Lung Cancer. Avoiding areas where people smoke, such as bars and restaurants, and seek out smoke-free options comes to aid.
02

High radon levels can be remedied to make your home safer.
03
01

Carcinogenic substances increase the risk of Lung Cancer. It is very important to take precautions to protect from exposure to toxic chemicals at work.
01

Opting for a healthy diet with a variety of fruits and vegetables rather that any supplements is a good way to prevent Lung Cancer.
03
01
What Are The Stages Of Lung Cancer?
The stage of Lung Cancer refers to the extent to which the cancer has spread in the body. Once the type of the Lung Cancer is determined, then the stage of the cancer is assigned. Stages for non-small cell Lung Cancers are different from small cell Lung Cancers. The stages listed below are taken from the National Cancer Institute’s Lung Cancer staging information:
- Limited stage: At this stage, cancer is restricted to only one side of the chest, typically in the lungs and lymph nodes. About 33% of cases with small cell Lung Cancer have limited stage cancer upon the first diagnosis.
- Extensive stage: At this stage, the cancer has spread throughout one lung, spread into both lungs, to lymph nodes on the other side of the chest or to other body parts. About 66% of small cell Lung Cancer cases have extensive stage cancer upon first diagnosis.
- Tumor (T) denotes the size of the tumor.
- Lymph node (N) indicates the presence of cancer in the lymph nodes.
- Metastasis (M) refers to whether cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
A number (0-4) or the letter X is added as a suffix to each factor indicating the severity of the disease. The letter X indicates that the information could not be assessed while 4 speaks of the high criticality of the disease. Once the T, N and M scores have been revealed, an overall stage is assigned.
Stages of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
Occult (hidden) stage: In this stage, cancer cells can be spotted in a sputum cytology exam or other test, though the tumor location could not be pinned.
Stage 0 (carcinoma in situ): Cancer cells are only found in the top layer of cells lining air passages and has not crept deeper into the lungs or spread beyond the air passages.
 Stage I: A tumor size may be either less than 3cm or range between 3 – 5 cm, but it has not spread to lymph nodes, making it possible for a surgeon to completely remove it. Stage I is divided into 2 sub-stages based on the size of the tumor:
Stage I: A tumor size may be either less than 3cm or range between 3 – 5 cm, but it has not spread to lymph nodes, making it possible for a surgeon to completely remove it. Stage I is divided into 2 sub-stages based on the size of the tumor:- Stage IA tumors are less than 3 cm wide.
- Stage IB tumors are more than 3 cm but less than 5 cm wide.
- Stage IIA: The Stage IIA tumor is discovered to be between 3 cm and 5 cm.
- Stage IIB: At this stage, the tumor is between 5 cm and 7 cm.
Stage III: Stage III Lung Cancer is found in both the lung and lymph nodes in the middle of the chest. This stage is further divided into two subsets.
- Stage IIIA: This defines a Lung Cancer that has spread on the same side of the chest from where it started.
- Stage IIIB: This defines a Lung Cancer in which the cancer has spread to either the opposite side of the chest or above the collar bone.
Stage IV: The 4th stage is the last and most advanced stage of Lung Cancer. The cancer can be any size, with any of the following characteristics:
- The cancer has spread to the opposite lung from where it began.
- Cancer cells have been discovered in the fluid surrounding the lung.
- Cancer cells have been discovered in the fluid surrounding the heart
Survival Rates Of Lung Cancer?
With no significant symptoms this hideous disease is difficult to detect in its early stages, and treatments for Lung Cancer in its later stages provide a poor prognosis. Lung Cancer has emerged as the leading killer of men and women stricken with invasive cancer.
| Stage | 5 year Survival Rate |
| 1A | 49% |
| 1B | 45% |
| 2A | 30% |
| 2B | 31% |
| 3A | 14% |
| 3B | 5% |
| 4 | 1% |
| Stage | 5 year Survival Rate |
| 1 | 31% |
| 2 | 19% |
| 3 | 8% |
| 4 | 2% |
Can Lung Cancer Be Detected Early?
As already mentioned, detecting Lung Cancer at an early stage is not that easy due to its silent nature. A screening test i.e. a procedure for critical evaluation for determining the presence, or spread of the tumor is sometimes helpful in early detection of Lung Cancer. At best, the screening methods find about 30% of Lung Cancers leaving the bulk i.e. rest 70% undetected. In addition, some test results are not clearly diagnostic which can lead to patient concerns and possibly unnecessary biopsies or surgeries. Screening for Lung Cancer is usually accomplished using three methods.

A physical exam is conducted to look for signs of wheezing, shortness of breath, cough, pain and other possible signs of Lung Cancer. The physical exam will also include the patient’s history of smoking and a chest X-ray.

A sputum cytology exam involves a microscopic examination of a patient’s mucus (sputum).

In this procedure, a detailed image of the body’s internal workings is taken. The images are then linked to an X-ray machine to create 3D images of the internal organs. These images may reveal potentially cancerous tumors.

If the screening tests suggest the possibility of Lung Cancer, definitive diagnostic tests may be done by a pathologist. The pathologist will examine the patient’s lung cells in sputum, phlegm, or from a biopsy sample to type and stage the Lung Cancer.

In biopsy, a tissue sample is taken from the suspected cancer. In general, lung biopsies are obtained by either needle biopsy, a lung bronchoscopy technique, or by surgical removal of tissue. Many other tests may be done to get more information about the cancer’s spread.
What Are The Treatments Available?
Adrenal glands are located deep within the body which makes it difficult to detect the growing tumors. However, if the tumor interferes with the regulation of hormones then some symptoms might be visible. There are multiple tests and examinations to ascertain the cause of these symptoms.
- Surgery to remove the entire lobe, in which the tumor is located, is the primary treatment for patients with early-stage cancer. The goal of surgery is to totally eliminate all the tumor cells and thereby provide a cure. The location and size of a lung tumor dictate how extensive the operation must be. Open thoracotomy or less invasive video-assisted thoracic surgery, using smaller incisions, may be recommended for appropriately selected patients.
- Lobectomy means the removal of an entire lobe of the lung. The mortality risk is 3% to 4%, and tends to be highest in older patients.
- Radiation therapy: In this procedure, high-energy x-rays are used to destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells. Radiation therapy is very useful in Lung Cancer treatment and can be implemented at different phases:
- As primary treatment
- Before surgery to shrink the tumor
- After surgery to eliminate any cancer cells that remain in the treated area
- To treat Lung Cancer that has spread to the brain or other areas of the body
- Advanced Lung Cancer Treatment: Most small cell and non-small-cell Lung Cancers can be treated with chemotherapy; they may also be treated with radiation therapy and surgery. In many patients with advanced disease, these methods may be used together, depending on the patient’s condition and recommendations by their cancer doctors.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the use of anti cancer drugs to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. The most common chemotherapy drugs used for treating NSCLC are:
- Cisplatin
- Carboplatin
- Paclitaxel
- Albumin-bound paclitaxel
- Docetaxel
- Pemetrexed
- Gemcitabine
- Vinorelbine
- Irinotecan
- Etoposide
- Vinblastine
- Targeted Lung Cancer Therapies: Targeted therapies are designed to prevent or stop Lung Cancer cells from growing by targeting the new blood vessels that are needed to allow the cancer cells to survive and grow; other treatments target growth and multiplication of Lung Cancer cells by interfering with chemical signals required by growing or multiplying cancer cells.
- Erlotinib: Erlotinib is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor – protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It is used in treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell Lung Cancer.
- Gefitinib: It is classified as a signal transduction inhibitor (epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor). It is used for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell Lung Cancer, after failure of both platinum-based and taxane-based chemotherapies.
- Afatinib: In 2013, the FDA approved afatinib for the initial treatment of metastatic NSCLC. These drugs can be used along without chemo as first line of treatment.
- Gefitinib: In 2015, the FDA approved gefitinib for the first-line treatment of patients with NSCLC. Gefitinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can stop tumors from growing by blocking signals inside cancer cells.
- Bevacizumab: These are monoclonal antibodies (a man-made version of a specific immune system protein) that can kill cancer cells, block their growth, and keep cancer from spreading. These drugs are used to treat advanced NSCLC by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein that helps new blood vessels to form.
- Crizotinib: A treatment that has shown benefits for people with advanced non–small cell Lung Cancer who have the ALK gene mutation. Crizotinib works by blocking ALK and stopping the growth of the tumor.
- Ceritinib: This was approved in 2014 for people with metastatic ALK-positive Lung Cancer who cannot tolerate crizotinib or whose cancer continued to grow while being treated with crizotinib.
- Ramucirumab: This drug is also be used to treat advanced NSCLC. VEGF has to bind to cell proteins called receptors to act. This drug is a monoclonal antibody that targets a VEGF receptor. This helps stop the formation of new blood vessels. This drug is most often given after another treatment stops working. It is often combined with chemo.
- In March 2015, the FDA approved the immunotherapy nivolumab for the treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC which could not be treated with chemotherapy.
- In 2016, the FDA approved a new immunotherapy called pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced NSCLC. Its therapeutic activity is similar to that of nivolumab.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Lung Cancer Treatment?
The side effects of Lung Cancer treatment depend on the type of treatment opted and the tenure of the treatment. Some common side effects include:
- Hair loss
- Mouth sores
- Loss of appetite, tiredness, nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Increased chance of infections (from having too few white blood cells)
- High blood pressure
- Constipation
- Cough
- Bleeding
- Headaches
- Diarrhea
- Skin problem
- Changes in vision
These side effects are usually non persistent and fades away after treatment is finished. There are ways to lessen these side effects. For example, drugs can be used to help prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting.
In most cases the side effects goes away once treatment is over, but in some rare case it may last a long time. If the side effects persist then it is advised to report immediately so that they can be treated promptly.
Is There Curative Treatment For Lung Cancer?
Lung Cancer generally goes undetected till later stages when it becomes almost incurable. Also, Lung Cancers can’t be removed completely by surgery, there is a fair chance of resurrection. In cases when fortunately the cancer gets detected at an early stage, treatment depends on the patient’s overall health. If the patient is in fairly good health then chemotherapy (chemo) combined with radiation therapy is the preferred line of treatment.