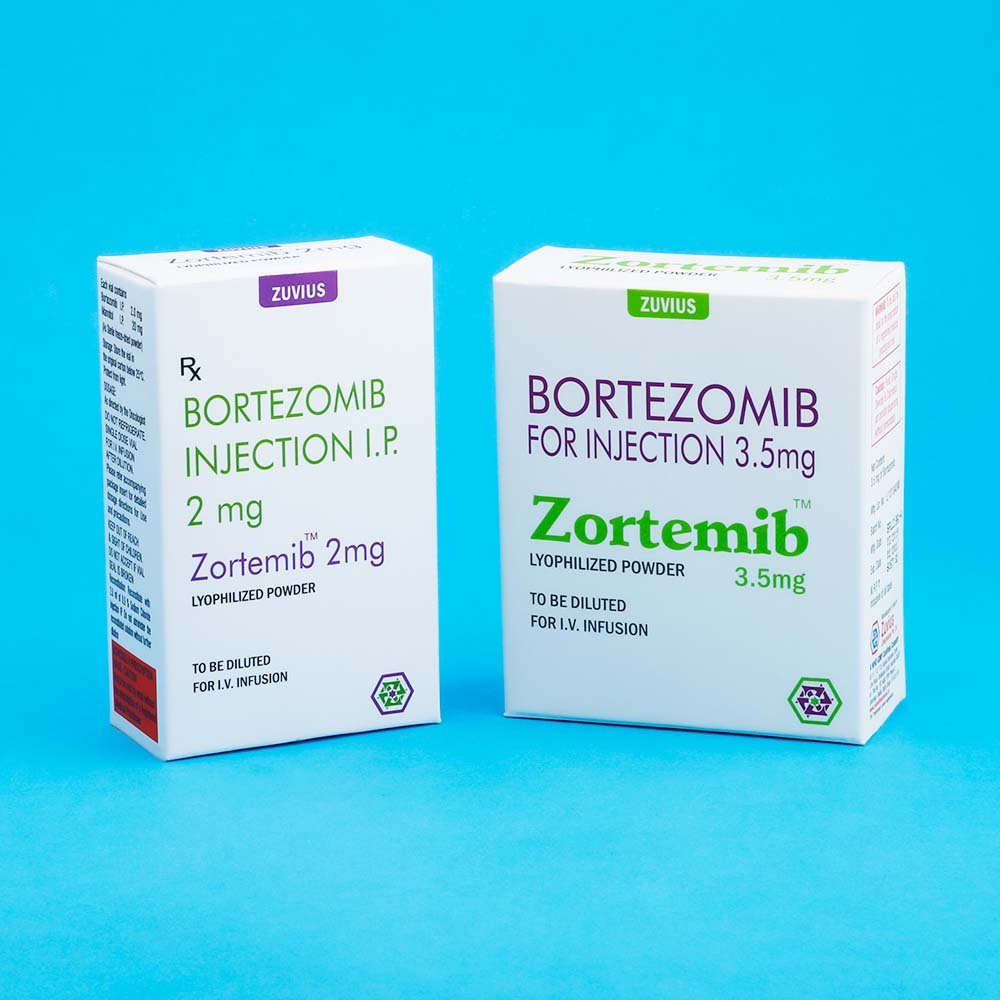
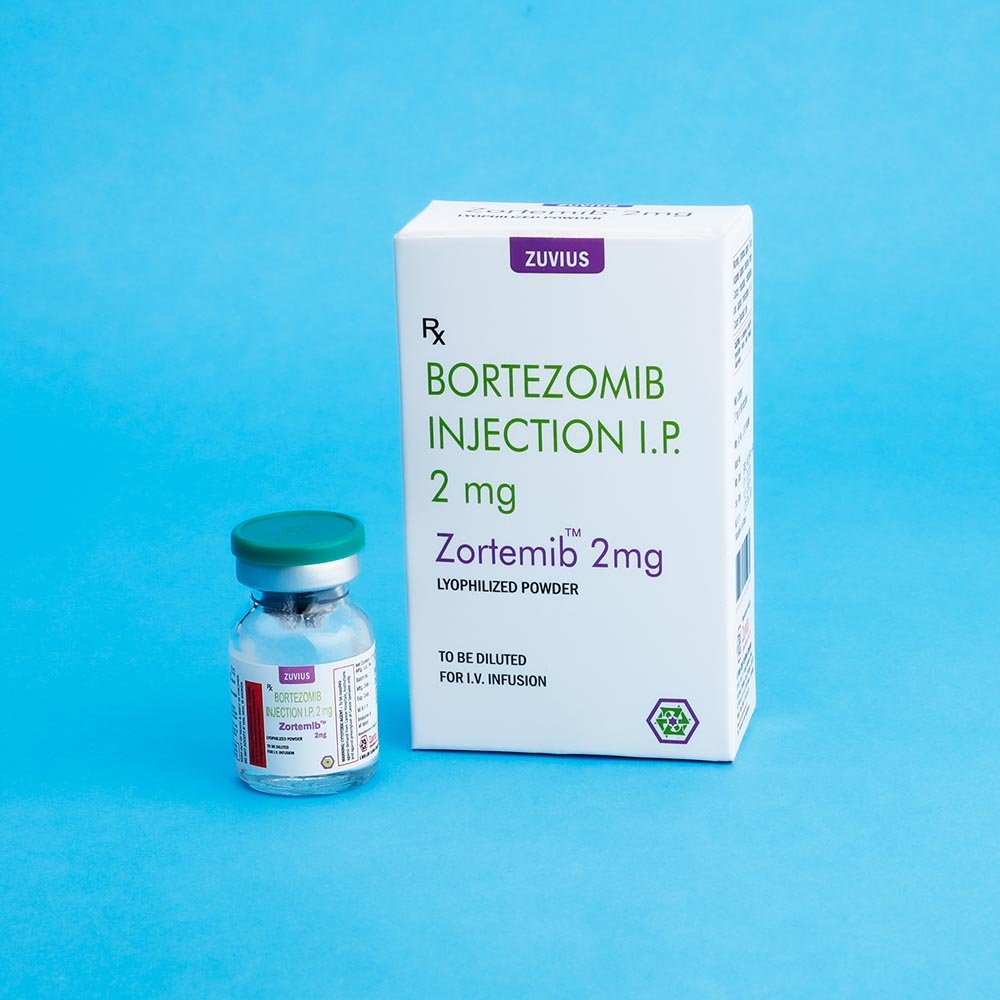
Zortemib
Bortezomib
Strength: 2mg / 3.5mg
Pack Size: 1 vial
Drug Class: protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Dosage and Administration:
Dosage in Previously Untreated Multiple Myeloma
(bortezomib) is administered as a 3-5 second bolus IV injection in combination with oral melphalan and oral prednisone for nine 6 week treatment cycles as shown in Tablet 1. In Cycle 1-4, is administered twice weekly (days 1, 4,8,11,22,25,29 and 32). In Cycle 5-9 is administered once weekly (day 1,8,22 and 29). At Least 72 hours should elapse between consecutive doses of Bortezomib
| Table 1-Dosage Regimen for patients with previously Untreated Multiple Myeloma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Twice weekly Bortezomib (cycles 1-4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bortezomib (1.3 mg/m2) | Day 1 | – | – | Day 4 | Day 8 | Day 11 | Rest Period | Day 22 | Day 25 | Day 29 | Day 32 | Rest Period | |||||||||||||
| Melphalan (9 mg/m2) Prednisone (60mg/m2) | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | – | – | Rest Period | – | – | – | – | Rest Period | |||||||||||||
| Once weekly Bortezomib (cycles 5-9 When used in combination with Melphalan and Prednisone | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bortezomib (1.3mg/m2) | Day 1 | `- | – | Day 8 | Rest Period | Day 22 | Day 29 | Rest Period | |||||||||||||||||
| Melphalan (9 mg/m2) Prednisone (60mg/m2) | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | – | – | Rest Period | – | – | – | – | Rest Period | |||||||||||||
Dose Modification Guidelines for Combination Therapy with Zortemib, Melphalan and Prednisone
Prior to initating any cycle of therapy with Bortezomib in combination with melphalan and prednisone
Platelet count should be 270 × 109/L and the ANC should be ≥ 1.0 × 109/L
Non – hematological toxicities should have resolved to grade 1 or baseline
| Table 2-Dose Modification During Cycles of Combination Bortezomib, Melphalan and Prednisons Therapy | ||
| Toxicity | Dose modification or delay | |
| For information concerning melphalan and prednisone, see manufacturing prescribing information | ||
| Hematological toxicity during a cycle : | ||
| If prolonged grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia ,or thrombocytopenia with bleeding is observed in the previous cycle | Consider reduction of the melphalan dose by 25% in the next cycle | |
| If platelet count ≤ 30 × 109/L or ANC ≤ 0.75 × 109/L on a Bortezomib dosing day (other than day 1) | Bortezomib dose should be withheld | |
| If several Bortezomib doses in consecutive cycle are withheld due to toxicity | Bortezomib dose should be reduced by 1 dose level (from 1.3mg/m2 to 1mg/m2, or from 1 mg/m2 to 0.7 mg/m2. | |
| Grade ≥ 3 non-hematological toxicities | Bortezomib therapy should be withheld until symptoms of the toxicity have resolved to Grade 1 or baseline. Then Bortezomib may be reinitiated with one dose level reduction (from 1.3mg/m2 to 1 mg/m2,or from 1 mg/m2 to 0.7mg/m2).Bortezomib –related neuropathic pain and/or peripheral Neuropathy ,hold or modify Bortezomib as outlined in table 3 | |
Dosage in Relapased Multiple Myeloma and Mantle cell Lymphome:Boetezomib (1.3mg/m2/dose) is administered as a 3 to 5 second bolus intravenous injection twice weekly for 2 weeks (Day 1, 2, 8 and 11) followed by a 10-day rest period (Days 12-21). For extended therapy of more than 8 cycles weekly for 4 weeks (Days 1, 8, 15 and 22) followed by a 13-days rest period (Days 23 to 35). At least 72 hours should elapse between consecutive doses of Bortezomib.
Dose Modification Guidelines for Relapsed Multiple Myeloma and Mantle Cell Lymphoma:
Bortezomib therapy should be withheld at the onset of any grade 3 non-hematological or Grade 4 hematological toxicities excluding neuropathy as discussed below. Once the symptoms of the toxicity have resolved. Bortezomib therapy may be reinitiated at a 25% reduced dose (1.3 mg/m2/dose reduce to 1mg/m2/dose reduced to 0.7 mg/m2/dose)
For the management of patients who experience. Bortezomib related neuropathic pain and/or peripheral neuropathy see Table 3. Patients should be treated with Bortezomib only after careful risk –benefit assessment.
| Table 3. Recommended Dose Modification for Bortezomib related Neuropathic Pain and/or Peripheral Sensory or Motor Neuropathy | ||
| Severity of peripheral Neuropathy sign and Symptoms | Modification of Dose and Regimen | |
| Grading based on NCI Common Toxicity Criteria CTCAE v3.0 | ||
| Grade 1 (paresthesisias , weakness and/or loss of reflexes ) without pain or loss of function | No action | |
| Grade 1 with pain or Grad 2 (interfering with function but not with activities of daily living) | Reduce Bortezomib to 1 mg/m2 | |
| Grade 2 with pain or Grade 3 (interfering with activities of daily living) | Withheld Bortezomib therapy until toxicity resolves. When toxicity resolves reinitiate with a reduced dose of Bortezomib at 0.7 mg/m2 and change treatment schedule to once per week | |
| Grade 4 (sensory neuropathy which is disabling or motor neuropathy that is life treating or leads to paralysis) | Discontinue Bortezomib | |
Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment:Patients with mild hepatic impairment do not required a starting dose adjustment and should be treated per the recommended Bortezomib dose. Patients with moderate pr severe hepatic impairment should be started on Bortezomib at a reduced dose of 0.7 mg/m2 per injection during the first cycle, and a subsequent dose escalation to 1.0 mg/m2 or further dose reduction to 0.5 mg/m2 may be considered based on patients tolerance (see Table)
| Table 4: Recommended Stating Dose Modification for Bortezomib in Patients with Hepatic impairment | ||||
| Abbreviation: S60T = serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase ; ULN = upper limit the normal range | ||||
| Bilirubin Level | S60T(AST ) Level | Modification of starting Dose | ||
| Mild | ≤ 1.0x ULN | >ULN | None | |
| >1.0x UNL 1.5x UNL | Any | None | ||
| Moderate | >1.5x-3.0 X UNL | Any | Reduce Bortezomib to 0.7mg/m2 in the first cycle. Consider dose escalation to 1.0 mg/m2 or further dose reduction to 0.5 mg/m2 in subsequent cycles based on patients tolerability | |
| Severe | >3x UNL | Any | ||
Administration Precautions:The drugs quality contained in one vial (3.5mg) may exceed the usal dose required. Caution should be used in calculating the dose to prevent overdose. ZORTEMIB is an antineoplastic. Procedure for proper handling and disposal should be considered .In clinical trials local skin irritation was reported in 5% of patients, but extravasation of ZORTEMIB was not associated with tissue damage.
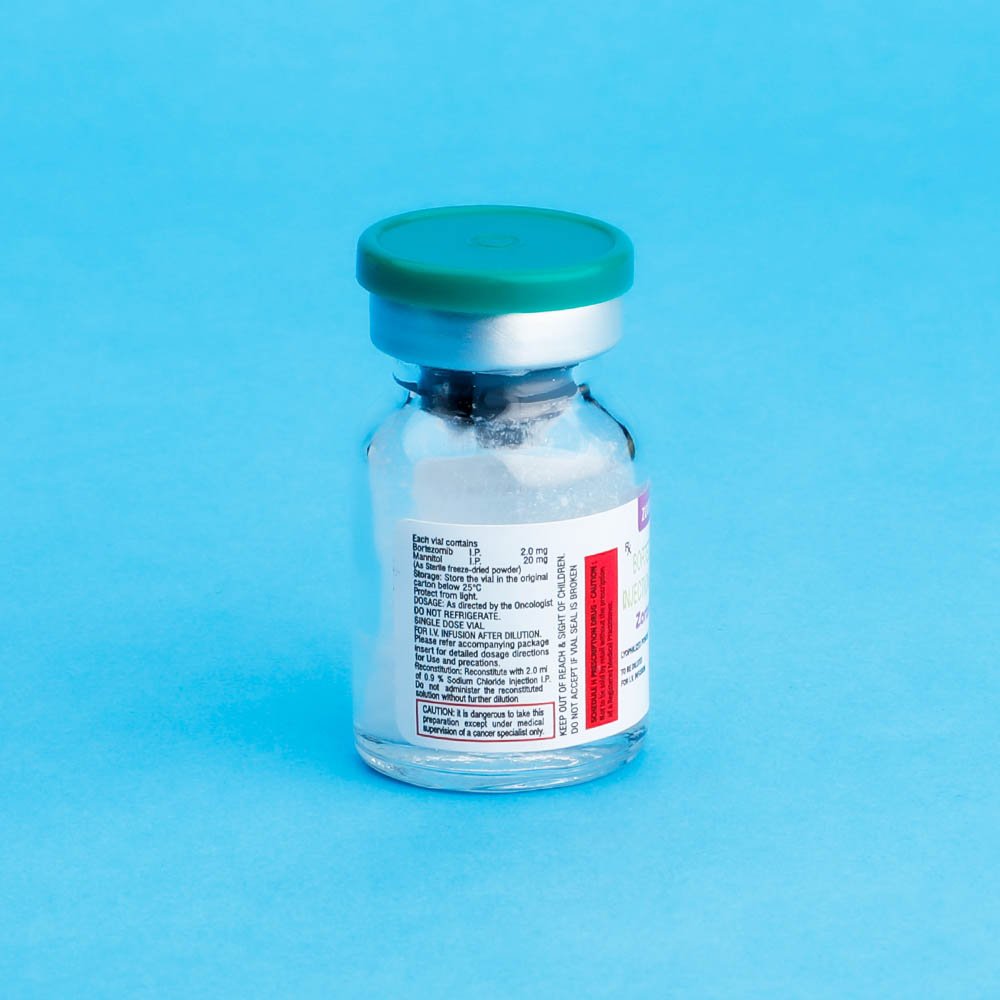
Reconstitution/Preparation for Intravenous Administration : Proper aseptic technique should be used. Reconstitute with 2ml of 0.9% Sodium Chloride resulting in a final concentration of 2mg/vial of bortezomib. The reconstituted product should be a clear and colorless solution.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. It any discoloration or particulate matter is observed the reconstituted product should not be used.
Stability : unopened vials of ZORTEMIB are stable until the date indicated on thepackage when stored in the original package protected from light.
ZORTEMIB contains no antimicrobial preservative. Reconstituted ZORTEMIB should be administered within 8 hours of preparation. When reconstituted as directe, ZORTEMIB may be stored at 25°C (77°F). The product may be stored for upto 8 hours in a syringe, however total storage time for the reconstituted material must not exceed 8hours when exposed to normal indoor lighting.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: Each single us a vial of ZORTEMIB contains 2mg of bortezomib as a sterile lyophilized powder.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: ZORTEMIB is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to bortezomib, boron or mannitol.
Cold Storage: no
Bortezomib for injection is an antineoplastic agent available for Intravenous Injection (IV) use only.
Each single use vials contains 2 mg of bortezomib as a sterile lyophilized powder. Bortezomib id modified dipeptidylboronic acid. The Product is provided as a mannitol boronic ester which, in reconstituted from, consist of the mannitol ester in equilibrium with its chydrolysis product, the
Monomeric boronic acid. The substance exits in its cyclic anhydride from as a trimericboroxine.
The chemical name for bortezomib, the monomeric boronic acid, is [(1R)-3-methyl-1[(2S)-1-oxo-3-phenyl-222-(pyrazinycarbony) amino]propyl]butyl] boronic acid.
Bortezomib has the following chemical structure:

The molecular weight is 384.24. The molecular formula is C19H25BN404. The solubility of bortezomib, as the monomeric boronic acid, in water is 3.3 to 3.8 mg/ml in a pH range of 2 to 6.5
Multiple Myeloma: (bortezomib) for injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least 1 prior therapy.
Mantle lymphoma: (bortezomib)for injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least 1 prior therapy.
Bortezomib, in particular has shown significant clinical efficacy in myeloma treatment. It is the most commonly used proteasome inhibitor and has been tested to be effective in prolonging the overall survival in several trials.
- The drugs quality contained in one vial (3.5mg) may exceed the usal dose required. Caution should be used in calculating the dose to prevent overdose. ZORTEMIB is an antineoplastic. Procedure for proper handling and disposal should be considered .In clinical trials local skin irritation was reported in 5% of patients, but extravasation of ZORTEMIB was not associated with tissue damage.Reconstitution/Preparation for Intravenous Administration : Proper aseptic technique should be used. Reconstitute with 2ml of 0.9% Sodium Chloride resulting in a final concentration of 2mg/vial of bortezomib. The reconstituted product should be a clear and colorless solution.Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. It any discoloration or particulate matter is observed the reconstituted product should not be used.Stability : unopened vials of ZORTEMIB are stable until the date indicated on thepackage when stored in the original package protected from light.ZORTEMIB contains no antimicrobial preservative. Reconstituted ZORTEMIB should be administered within 8 hours of preparation. When reconstituted as directe, ZORTEMIB may be stored at 25°C (77°F). The product may be stored for upto 8 hours in a syringe, however total storage time for the reconstituted material must not exceed 8hours when exposed to normal indoor lighting.DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: Each single us a vial of ZORTEMIB contains 2mg of bortezomib as a sterile lyophilized powder.CONTRAINDICATIONS: ZORTEMIB is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to bortezomib, boron or mannitol.WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: ZORTEMIB should be administered under the supervision of a physician experienced in the used of antineoplastic therapy. Complete blood counts (CBC) should be monitored frequently during treatment with ZORTEMIB.Use in PregnancyPregnancy Category D: Women of childbearing potential should avoid becoming pregnant while being treated with ZORTEMIB. Bortezomib administered to rabbits during organogenesis at a dose approximately 0.5 time the clinical dose of 1.3 mg/m2 based on body surface area caused post implantation loss and a deceased number of live fetuses.Peripheral Neuropathy: ZORTEMIB treatment causes a peripheral neuropathy that is predominantly sensory. However, cases of severe sensory and motor peripheral neuropathy have been reported. Patients with pre-existing symptoms (numbness, pain or a burning feeling in the feet or hands) and/or signs of peripheral neuropathy may experience worsening peripheral neuropathy (including≥ Grade 3) during treatment with ZORTEMIB. Patients should be monitored for symptoms of neuropathic pain or weakness. Patients experiencing new or worsening peripheral neuropathy may require change in the dose and schedule of ZORTEMIB. Following dose adjustments, improvement in or resolution of peripheral neuropathy was reported in 50% of patients with≥ Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy in the relapsed multiple myeloma study. Improvement in or resolution of peripheral neuropathy was reported in 73% of patients who discontinued due to Grade 2 neuropathy or who had≥ Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy in the phase 2 multiple myeloma studies. The long-term outcome of peripheral neuropathy has not been studied in mantle cell lymphoma.Hypotension:The incidence of hypotension (postural, orthostatic, and hypotension NOS) was 13%.Theses event are observed throughout therapy, caution should be used when treating patients with a history of syncope, patients receiving medications know to be associated with hypotension and patients who are dehydrated. Management of orthostatic/postural hypotension may include adjustment of antihypertensive medications, hydration, and administration of mineralocorticoids and/or sympathomimetic.Cardiac Disorder:Acute development or exacerbation congestive heart failure and new onset of decreased left ventricular ejection fraction have been reported, including reports in patients with a history of syncope, patients with risk factors for existing heart diseases should be closely monitored in the rerelapsed multiple myeloma study, the incidence of any treatment-emerged cardic disorder was 15% and 13% in the Zortemib and dexamethasone group, respectively. The Incidence of heart failure event (acute pulmonary edema, cardiac failure, congestive cardic failure. Cardiogenic shock, pulmonary edema) was similar in the Zortemib and dexamethasone group, 5% and 4% respectively .There have been isolated cases of Qt-interval prolongation in cinical studies, causality has not been established
Pulmonary Disorder:There have been reports of acute diffuse infiltrative pulmonary disease of unkown etiology such as Pnemounitis, interstitial pneumonia, lung infiltration and Acute Respiratory Distress syndrome (ARDS) in patients receiving Bortezomib. Some of these events have been fatal .
In a clinical trial, the first two patients given high0- dose cytarabine (2mg/m2 per day) by continues infusion with daunorubicinand Zortemib for relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia died of ARDS early in the course o therapy. There have been reports of pulmonary hypertension associated with ZORTEMIB administration in the absences of left heart failure or significant pulmonary diseases.
In the event of new worsening cardiopulmonary symptoms, a prompt comprehensive diagnostic evaluation should be conducted.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS): There have been reports of RPLS in patients receiving ZORTIMIB. RPLS is a rare, reversite, neurological disorder which can present with seizure ,hypertension, headache, lethargy, confusion blindness, and other visual and neurological disturbances brain imaging preferably MRI (Magnetic Rsonance Imaging), is used to confirm the diagnosis. In patients developing RPLS, discontinuous ZORTEMIB. The safety of reinitiating ZORTEMIB therapy in patients previously experiencing RPLS is not known.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Event:ZORTEMIB treatment can cause nausea, diarrhea, constipation and vomiting. Sometimes requiring use of antiemetic and anti diarrhea medications, lieus can occurs fluid and electrolyte replacement should be administered to prevent dehydration.
Thrombocytopenia/Neutropenia: ZORTEMIB is associated with thrombocytopenia and neutropenia that allow a cyclical with nadirs occurring following the last dose of each cycle and typically recovering prior to initiation of the subsequent cycle. The cyclical patterns of platelet and neutrophiil decreases and recovery remaindconsistent over the 8 cycle of twice weekly dosing. And there were no evidences of cumulative thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. The mean platelet count nadir measured was approximately 40% of baseline. The seventy of thrombocytopenia related to pretreatment platelet count is shown in Tablet 5. In the relapsed multiplies mymeloma study, the incidences of significant bleeding event (≥Grade 3) was similar on both the ZORTEMIB (4%) and dexamethasone (5%) arms. Platelet count should be monitored prior to each dose of ZORTEMIB. Patients experiencingthrombocytopenia may require change in the dose and schedule of ZORTEMIB. Transfusion may be considered .The incidence of febrile neutropenia was <1%
Tablet 5 Severity of Thrombocytopenia Related to pretreatment patients count in the Relapsed Multiple Myeloma study Pretreatment Platelet Count * Number of patients (N=331)** Number (%) of patients with Platelet count <10,000/µL Number (%) of patients with platelet count 10,000-25,000/-L *A baseline platelet count of 50,000/µL. was required for study eligibility **Data were missing at baseline for 1 patients ≥75,000/µL 309 8(3%) 36(12%) ≥50,000/µL≥75,000/µL 14 2(14%) 11(79%) ≥10,000/µL 7 1(14%) 5(71%) Tumor Lysis Syndrome:Because Bortezmib is cytotoxic agent and can rapidly kill malignant cells, the complications of tumor lysis syndrome may occure. Patients at risk of tumor lysis syndrome are those with high tumor burden prior to treatment. These patients should be mentioned closelyand appropriate precaution taken.
Hepatic event:Cases of acute liver failure have been reported in patients receiving multiple concomitant medications and with serious underlying medical conditions. Other reported hepatic event include increases in liver anzymes, hyperbilirubinemia, and hepatic. Such changes may be reversible upon discontinuation of BORTEZMIB. There is limited re-challenge information in these patients.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment: Bortezomib is metabolized by liver enzymes. Bortezomib exposure is increased in patients with moderate of severe hepatic impairment these patients should be treated with ZORTEMIB at reduced starting doses and closely monitored for toxicities.
This medicine may cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea, so it is important to drink plenty of fluids. It may also cause stomach or bowel blockage. If you experience dizziness or lightheadedness, contact your doctor.