Sinus Cancer
What Is Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer?
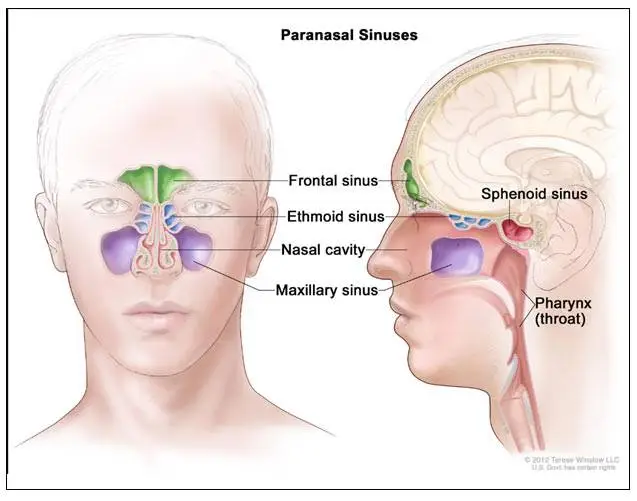
The nasal cavity is the space just behind the nose through which air passes to the throat. The Paranasal Sinuses are air-filled areas that surround the nasal cavity. There are several Paranasal Sinuses named after the bones that surround them:
- Frontal Sinuses are in the lower forehead above the nose.
- Maxillary Sinuses are in the cheekbones on either side of the nose.
- Ethmoid Sinuses are beside the upper nose, between the eyes.
- Sphenoid Sinuses are behind the nose, in the center of the skull.

The types of Sinus Cancer include:

Squamous cell carcinoma
This is the most common type of nasal cavity and paranasal Sinus Cancer. Squamous cells are flat cells that make up the thin surface layer of the structures of the head and neck.

Adenocarcinoma
This is the second most common type of nasal cavity and paranasal Sinus Cancer. It begins in gland cells.

Melanoma
Melanoma develops from cells called melanocytes that give the skin its color. It is usually an invasive, fast-growing cancer. However, it only accounts for about 1% of tumors found in this area of the body.

Inverting papilloma
These are benign, wart-like growths that may develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Approximately 10% to 15% of these will develop into cancer.

Esthesioneuroblastoma
This type of cancer is related to the nerves that control the sense of smell. It occurs on the roof of the nasal cavity and involves a structure called the cribriform plate. The cribriform plate is a bone located deep in the skull between the eyes and the sinuses.

Midline granuloma
A group of several unrelated conditions that cause the breakdown of the healthy tissue of the nose, sinuses, and nearby tissues. Some cases are due to immune system problems, and many others are actually a type of lymphoma (see below).

Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system carries lymph, a colorless fluid containing lymphocytes. Lymphoma may develop within the lymph tissue found in the lining of the nasal cavity and Paranasal Sinuses, called the mucosa.

Sarcoma
Sarcoma is a type of cancer that begins in muscle, connective tissue, or bone.
Anatomy Of Adrenal Cancer
Occurrence Rates
- 30 to 40% will have it in their maxillary sinuses.
- 40 to 50% will develop it in their nasal cavity.
- 10 to 15% will have the cancer in their ethmoid sinuses.
What Are The General Symptoms Of Sinus Cancer?
POSSIBLE SYMPTOMS OF SINUS CANCER INCLUDE:
- A lump or sore inside the nose that does not heal.
- A lump on the face or roof of the mouth.
- Numbness or tingling in the face.
- Swelling or other trouble with the eyes, such as double vision or the eyes pointing in different directions.
- Pain or pressure in the ear.
- Nasal obstruction or persistent nasal congestion and stuffiness, which is often called sinus congestion
- Chronic sinus infections that do not respond to antibiotic treatment.
- Frequent headaches or pain in the sinus region.
- Pain or swelling in the face, eyes, or ears.
- Persistent tearing of the eyes.
- Bulging of one of the eyes or vision loss.
- Decreased sense of smell.
- Pain or numbness in the teeth.
- Loosening of teeth.
- A lump on the face, nose, or inside the mouth.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Difficulty opening the mouth.
- A lump or sore inside the nose or neck that does not heal.
- Fatigue.
What Are The General Causes Of Sinus Cancer?
Sinus Cancer is associated to a number of artificial causatives that can be controlled to avoid the disease. However, many people with one or more risk factors never get cancer, while others who get cancer may have had few or no known risk factors.
There are 2 risk factors that greatly increase the risk of Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer:

Use of tobacco is the single largest risk factor for head and neck cancer. Tobacco products include cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, and snuff. Eighty-five percent (85%) of Sinus Cancer is linked to tobacco use.

Frequent and heavy consumption of alcohol is a high risk factor for Sinus Cancer. Using alcohol and tobacco together increases this risk even more.
Other factors can raise a person’s risk of developing Nasal Cavity or Paranasal sinus cancer.

Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer occurs twice as often in men as in women.

Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer are most commonly found in people between the ages of 45 and 85. However, the development of this cancer is also found among younger people now a days.

Infection with this virus is a risk factor for Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer.

Breathing in certain substances, most commonly found work environments, may increase the risk of developing Nasal Cavity or Paranasal Sinus Cancer. These substances include:
- Dust from the wood, textiles, or leather industries
- Flour dust
- Nickel dust
- Chromium dust
- Mustard gas
- Asbestos
- Rubbing alcohol, also called isopropyl alcohol, fumes
- Radium fumes
- Glue fumes
- Formaldehyde fumes
- Solvent fumes used in furniture and shoe production


Can Sinus Cancer Be Prevented?
Though some of the causatives of sinus cancer are beyond our control but most of them are controllable.
- The two major known causes of sinus cancer are usage of tobacco and alcohol. So, by lowering and controlling their consumption one can definitely be prevented.
- Using marijuana also increases the risk, so saying no to marijuana drops the risk.
- Ensuring safe sex reduces the risk of HPV.
- Ensuring safe work and home environment free of air pollutants.
What Are The Stages Of Sinus Cancer?
- T refers to the spread of cancer cells to tissues next to the testicle.
- N describes the spread of cancer cells to regional lymph nodes.
- M indicates whether the cancer has metastasized.
The results are combined to determine the stage of cancer for each person. There are 5 stages for nasal cavity and paranasal Sinus Cancer: stage 0 (zero) and stages I through IV (1 through 4).
- T1: The spread of tumor is limited to the inside of the sinus.
- T2: The tumor has spread to the bone surrounding the sinuses.
- T4a: The tumor has invaded the bone surrounding the eye, the skin of the cheek, or the throat.
- T4b: The tumor might invade: the back of the eye, the brain area, or the bones of the skull.
- T1: The tumor is limited to the inside of the sinus and has no involvement with the bone.
- T2: The tumor extends into the nasal cavity.
- T3: The tumor extends into the maxillary sinus or to the bone surrounding the eye.
- T4a: The tumor has spread throughout the facial bones or into the base of the skull.
- T4b: The tumor invades any of the following: the back of the eye, the brain area, or the back of the head.
- NX: The regional lymph nodes cannot be evaluated.
- N0: There is no evidence of cancer in the regional lymph nodes.
- N1: The cancer has grown up to 3 cm and has spread to a single lymph node on the same side as the primary tumor.
- N2a: The cancer sizes from 3 cm to 6 cm and has spread to a single lymph node on the same side as the primary tumor.
- N2b: The cancer has spread to more than 1 lymph node on the same side as the primary tumor, but none measures larger than 6 cm.
- N2c: The cancer has spread to more than 1 lymph node on either side of the body, but none measures larger than 6 cm.
- N3: The cancer is found in at least 1 nearby lymph node and is larger than 6 cm.
- MX: Distant metastasis cannot be evaluated.
- M0: The cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
- M1: The cancer has spread to another part(s) of the body.
- GX: The grade cannot be evaluated.
- G1: The cells look more like healthy tissue and are well differentiated.
- G2: The cells are only moderately differentiated.
- G3: The cells don’t resemble healthy tissue and are poorly differentiated.
@ 2005 American Society of Clinical Oncology
This is an invasive cancer (T4a) that either has no lymph node involvement (N0) or has spread to only 1 same-sided lymph node (N1) but with no metastasis (M0). It is also used for any cancer (any T) with more significant nodal involvement (N2) but with no metastasis (M0).
@ 2005 American Society of Clinical Oncology
This is an invasive cancer (T2) that has not spread to lymph nodes (N0) or to distant parts of the body (M0).
@ 2005 American Society of Clinical Oncology
This is an invasive cancer (any T) that has spread to lymph nodes (any N) but has no metastasis (M0). It is also used for any cancer (any T) that is found in lymph nodes and is larger than 6 cm (N3) but has no metastasis (M0).
@ 2005 American Society of Clinical Oncology
This includes invasive cancer (T3) with no spread to regional lymph nodes (N0) and no metastasis (M0), as well as invasive cancer (T1, T2, T3) that has spread to regional lymph nodes (N1) but shows no sign of metastasis (M0).
@ 2005 American Society of Clinical Oncology
This refers to any tumor (any T, any N) when there is evidence of distant spread (M1).
@ 2005 American Society of Clinical Oncology
Survival Rates Of Sinus Cancer?
| Stages | 5-year relative survival rate |
| I | 63% |
| II | 61% |
| III | 50% |
| IV | 35% |
The survival rate and diagnosis usually go hand in hand. If the symptoms and stage of Sinus Cancer are discovered earlier, the individual will have a greater chance of survival. Here is an analysis of 5 year survival rate of different types of Sinus Cancer based on earlier history. However, these rates might go up and down when calculated for a particular area.
Can Sinus Cancer Be Detected Early?
Small cancers of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses usually do not cause any specific symptoms. Many of these cancers are not found until they have grown large enough to block the nasal airway or sinuses, or until they have spread to nearby tissues or even to distant areas of the body.
Here are a few diagnostic tests that might be recommended to detect the presence of this disease.
- Screening : Screening refers to tests and exams used to detect cancer, in people who do not have any symptoms. Screening can find some types of cancer early, when treatment is most likely to be effective.
- Physical examination: During a physical examination, any lump on the neck, lips, gums, and cheeks is checked. The doctor further inspects the nose, mouth, throat, and tongue for abnormalities, often using a light and/or mirror for a clearer view.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy : The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle.
- Incisional biopsy : The removal of part of an area of tissue that doesn’t look normal.
- Excisional biopsy : The removal of an entire area of tissue that doesn’t look normal.
- Endoscopy: An endoscopy allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called an endoscope.
- Nasoscopy : It is a procedure to look inside the body for abnormal areas. A thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing is inserted into the nose.
- X-ray: An x-ray is a way to create a picture of the structures inside of the body, using a small amount of radiation
- Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan: A CT scan creates a 3-dimensional picture of the inside of the body using x-rays taken from different angles.
- Laryngoscopy: It is a procedure to look at the larynx for abnormal areas. A mirror or a laryngoscope is inserted through the mouth to see the larynx.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI uses magnetic fields, to produce detailed images of the body, especially images of soft tissue, such as the eye in its socket and the part of the brain near the sinuses.
What Are The Treatments Available?
Depending on the type of Cancer and how far it has spread, different treatments are employed to cure or retard the growth and spread of the disease. Here are a few treatment options usually opted by doctors or oncologists.
Here are a few diagnostic tests that might be recommended to detect the presence of this disease.
- Excision: An operation to remove the cancerous tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it is conducted.
- Maxillectomy: This is a surgery that removes part or all of the hard palate, the bony roof of the mouth. Artificial devices called prostheses or, flaps of soft tissue with and without bone can be placed to fill gaps.
- Endoscopic sinus surgery: This is less destructive to healthy tissue than traditional operations. Occasionally, it can be used for benign tumors. The surgeon makes a small incision to remove the tumor using a thin, telescope-like tube inserted into the nasal cavity or sinus.
- Neck dissection: This is the surgical removal of lymph nodes in the neck area.
- Reconstructive surgery: It may be recommended when surgery requires removing large or specific areas of tissue.
- External-beam radiation therapy: External-beam radiation therapy is the most common type of radiation given from a machine outside the body. Specific types of external radiation therapy include:
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
- Proton therapy.
- Internal radiation therapyRadiation treatment given using implants, it is called internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. Internal radiation therapy involves tiny pellets or rods containing radioactive materials that are surgically implanted in or near the tumor. The implant is left in place for several days while the person stays in the hospital.

Early stage of the Sinus Cancer is small, localized, and highly curable when treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Advancement in science and technology is facilitating modern methods of highly successful treatment.
01

Spotting any of the symptoms of nasal cancer or having a doubt in your mind calls for a visit to the doctor. Also, a familial history or personal history of the disease commands a regular examination at least once a year or as per the doctor’s advice.
02

Consulting a doctor or oncologist in case of any indication felt or experienced that might suggest the presence of the disease. Ignoring even a small indication might result in devastation. In early stages sinus cancer is highly curable but it gets complicated with passing time.
