What Is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder
Bladder is a hollow muscular balloon-shaped organ, located in the lower part of the abdomen behind the pubic bone.
Also know more about : Bone Cancer
Layers of the Bladder
- The primary function of the Bladder is to store urine.
- Urine made by the kidneys is passed to the Bladder through the ureters. The Bladder is lined by layers of muscle tissues that can stretch to accommodate the urine. During urination, the muscles of the Bladder contract to release the urine.

Bladder Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in any part of the body. These cells accumulate and form a tumor. The tumor may be benign or malignant in nature. Benign tumors are less invasive and their growth is limited to the site of origin, whereas malignant tumors are the ones that possess a greater threat. Malignant tumors grow and continue to spread through different parts of the body if left untreated.
When such a tumor is formed in the Bladder then it is termed as Bladder Cancer. Bladder Cancer refers to several types of malignant growth of the Urinary Bladder. Depending on the cells, Bladder Cancer is categorized into different types and each type demands a unique prognosis.
Anatomy of Bladder
The above image is used for educational purpose only.

Types of Bladder Cancer
- Urothelial carcinoma(transitional cell carcinoma): Urothelial is the most prevalent Bladder Cancer and it accounts for more than 90% of all Bladder Cancers. This Cancer begins in urothelial cells that line the interior of the Bladder and are responsible for stretching and changing shape when the Bladder is full. Urothelial carcinoma is further classified into:
- Non-invasive urothelial carcinoma: The Cancer is limited to the urothelium and has not spread to the muscle layer, though it may spread into the lamina propria beneath the transitional cells.
- Invasive urothelial carcinoma: The Cancer spreads to the Bladder’s muscular propria and sometimes to the surrounding tissues.
- Papillary urothelial carcinoma: A noninvasive papillary tumor grows into the hollow center of the Bladder on a stalk. Invasive papillary urothelial carcinoma can spread into the lamina propria or muscle layer.
- Flat urothelial carcinoma: Noninvasive flat urothelial carcinoma grows in the layer of cells closest to the inside of the Bladder and appears as flat lesions on the inside surface of the Bladder. Invasive flat urothelial carcinoma may invade the deeper layers of the Bladder, particularly the muscular layer.

Squamous cell carcinoma
These Cancers are rare but invasive and account for 3 – 8% of Bladder Cancers. It is mainly caused due to Bladder inflammation or irritation for a long period. These cells grow in flat masses of interconnected cells.

Adenocarcinoma
It is a rare and invasive form of all Bladder Cancer and accounts for only 2% of all Bladder Cancer cases. These Cancers occur in the glandular cells.

Small cell carcinoma
Small-cell carcinomas contribute to less than 1% of Bladder Cancer. Its origins in nerve-like cells called neuroendocrine cells. These Cancers often grow quickly and are very invasive.
Occurrence Rate of Bladder Cancer in India
Bladder Cancer is one of the most common urinary tract Cancers. According to the recent reports from National Cancer Registry Programme, the overall occurrence of Bladder Cancer in India is 2.25%. According to Cancer statistics of the world, Bladder Cancer ranks 9th in occurrence. Detailed statistics revealed, it is the 7th most common malignancy in men and 17th in women.
prognosis, advance diagnosis, and therapies along with low cost facilitates are the perks of the healthcare facilities in the country.
What Are The General Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer?
A symptom is an abnormal sign that a person experiences when any of the organs fail to perform its functions perfectly. Bladder Cancer often shows early symptoms facilitating early detection. Some of the symptoms that demands a cross-check for the presence of any malicious cells are:
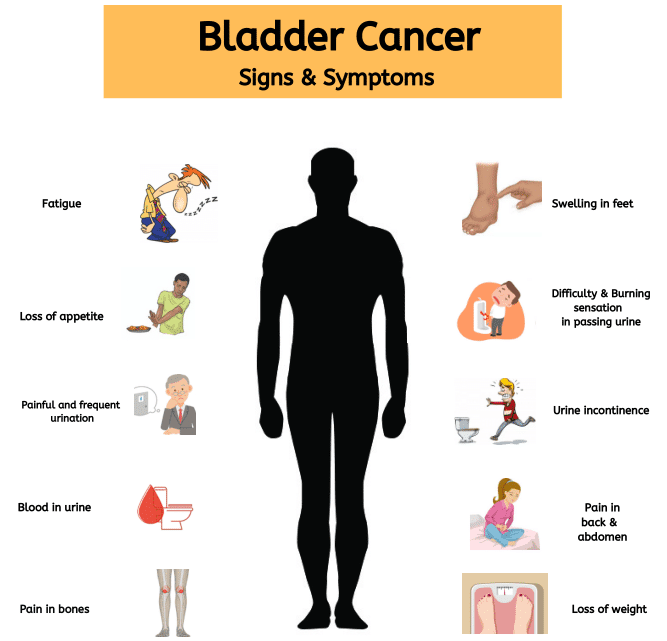
Symptoms of early Bladder Cancer
- Hematuria i.e blood in the urine with or without clots.
- Changes in Bladder habits or symptoms of irritation
- Increased frequency and urgency of urination
- Pain or burning during urination
Symptoms of advanced Bladder Cancer
- Being unable to urinate
- Lower back pain on one side
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Swelling in the feet
- Bone pain
Any blood in the urine should be reported to the doctor immediately, though this does not certainly claim the presence of Bladder Cancer. Less than 0.1% of cases of Hematuria are caused by Bladder Cancer. However, this sign should not be ignored. Blood in the urine may be a sign of several other medical conditions, as well as Bladder Cancer.

What Are The General Causes Of Bladder Cancer?
The exact cause of Bladder Cancer has not yet been coined down. However, over the years certain factors have been identified to have increased the risk of developing Bladder Cancer. Bladder Cancer can be caused by multiple factors. An unhealthy lifestyle, familial history, and ignorance are the most common modes of getting this disease. However, there are certain factors that are natural and are beyond one’s control.
- The greatest risk factor of Bladder Cancer is the smoking of cigarettes, bidis, and hookah.
- Exposure to certain chemicals such as dyes, metal, paints, leather, textile, and organic chemicals is another causative factor.
- Gender and age also play an important role. Men are four times more likely to develop this disease. Also, the risk increases with increasing age.
- Infection with schistosomiasis is a cause of this Cancer.
- An unhealthy diet and no or limited physical activities also increase the risk of developing Bladder Cancer.
- Personal history of Bladder or other urothelial Cancer may cause the recurrence of Bladder Cancer.
- Bladder birth defects
- Genetics and family history
- Arsenic in drinking water
- Low Fluid Consumption
Can Bladder Cancer be prevented?
Due to ambiguity in the exact causes of Bladder Cancer , preventions of Bladder Cancer is difficult. However avoiding the risk factors do provide a shielding to some extent. Some of the precautions are listed below:
- Chemicals like aromatic amines, such as benzidine and beta-naphthylamine can cause Bladder Cancer. So staying away and taking preventive measures may help in preventing Bladder Cancer.
- Quit smoking.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and indulging in regular physical activities.

What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer?
- A tumor (T): It describes the size of the tumor and the location of the tumor.
- Node (N): It depicts the extent to which the malignant cells have spread.
- Metastasis (M): It denotes if the Cancer cells have metastasized to other parts of the body.
Bladder Cancer is staged into 5 groups, which is determined by the extent of the tumor and its spread. The following list describes its various stages.
- Stage 0 (Ta, N0, M0): This is the earliest stage of Bladder Cancer. Cancer cells are diagnosed only on the inner surface of the Bladder. Cancer cells are grouped together and can easily be removed by surgery.
- Stage 0is (Tis, N0, M0): At this stage, cancer cells are found only on the inner lining of the Bladder. This is a high-grade Cancer and is an aggressive one as it often leads to muscle-invasive disease.
- Stage I (T1, N0, M0): Cancer cells have penetrated the inner lining of the Bladder but have not reached the muscular layer.
- Stage II (T2, N0, M0): Cancer cells have spread into the thick muscle wall of the Bladder. It is also called invasive Cancer or muscle-invasive Cancer.
- Stage III (T3/T4a, N0, M0): Cancer cells have spread beyond the Bladder muscle and into the outer layer of tissue surrounding the Bladder. It may also have spread to the prostate in a man or the uterus and vagina in a woman.
- Stage IV: Cancer cells have spread towards the abdominal or pelvic wall. In men, the Cancer cells may spread to the prostate. In women, the Cancer cells may spread to the uterus or vagina. Cancer cells may have also spread to the lymph system and metastasized to other parts of the body.
Survival Rates Of Bladder Cancer?
| Stage | Survival Rate |
| 0 | 98% |
| I | 88% |
| II | 63% |
| III | 46% |
| IV | 15% |
The rate decreases progressively with the passage of each stage. Stage III is considered critical, while stage IV is, more often than not, fatal. The 5-year survival rate refers to the percentage of patients who live at least 5 years after their cancer is diagnosed. Of course, many people live much longer than 5 years (and many are cured).
The numbers below are based on thousands of people diagnosed with Bladder Cancer from 1988 to 2001. These numbers come from the National Cancer Institute’s SEER database.
Can Bladder Cancer Be Detected Early?
The advancement in science and technology has facilitated multiple convenient ways to diagnose Bladder Cancer at a very early stage thus making its prognosis easier. Here are a few tests which are used to diagnose Bladder Cancer :
Urine Sample: Urine tests are conducted to check for abnormal cells, this called a urinary cystography. Though this test reveals some important information, however, the accuracy of the same is doubtful.
Physical examination : This may include an examination of the rectum and vagina for women, and just the rectum for men.
Imaging Tests: These tests allow the doctor to observe the structures of the urinary tract. A dye is either injected into a vein or swallowed directly, to highlight the Bladder, uterus, and kidneys. An X-ray is then taken to get a clear view of the suspected organs.
Cystoscopy: A long-thin flexible tube is inserted through the patient’s urethra into the Bladder to look inside it. A cystoscope has a lens for viewing and a fiber-optic lighting system which allows observing the inside of the Bladder and urethra.
Biopsy: Biopsy is a procedure in which a few cells or tissues are removed and observed under a powerful microscope. This procedure is also called TURBT (transurethral resection of bladder tumor). TURBT is sometimes used to treat Bladder Cancer. The patient is usually given a general anesthetic.

What Are The Treatments Available?
There are different types of treatments available to cure Bladder Cancer. Depending on the overall health condition, age, and health history of the patient the most suitable treatment plan is selected by the oncologists. Some of the advanced treatment options are:
Surgery: It is the most preferred treatment option when Cancer is detected at an early stage. Surgery involves removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissues. There are different types of surgeries categorized based on stage and grade of the disease.

This surgery is conducted to route a new path for the urine to pass out of the body. This becomes necessary if a major portion of the Bladder is removed through surgery as a treatment to Bladder Cancer.
In this surgery, a cystoscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. An optical tool is then used to remove cancer or to burn the tumor with high-energy electricity. This process is also known as fulguration.
- Transurethral Bladder tumor resection (TURBT): In this procedure, a cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the Bladder. The surgeon then removes the tumor using a laser, or fulguration.
- Radical cystectomy: This is a surgery to remove the whole Bladder along with any lymph nodes and nearby organs having Cancerous cells. This surgery generally opts when the Bladder Cancer invades the muscle wall or a large portion of the Bladder. In men, generally, the prostate and the seminal vesicles are removed while in women, the uterus, the ovaries, and part of the vagina are removed.
- Partial cystectomy: This involves removing a part of the Bladder. This surgery usually opts for those patients who have a low-grade tumor that has invaded the wall of the Bladder but is limited to one area of the Bladder. This is also called segmental cystectomy.

Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. A chemotherapy regimen typically consists of a specific number of cycles given over a set period of time.
There are 2 types of chemotherapy that may be used to treat Bladder Cancer.
Intravesical chemotherapy
In this therapy, drugs are delivered into the Bladder through a catheter that has been inserted through the urethra. Local treatment only destroys superficial tumor cells that come in contact with the chemotherapy solution.
Systemic chemotherapy
When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body then it is called systemic chemotherapy.
Regional chemotherapy
When chemotherapy is placed directly into an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas then it is called regional chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the patient’s immune system to fight Cancer. It boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight the Cancer. It uses materials made either by the body or in a laboratory to improve, target, or restore immune system function. This type of Cancer treatment is also called biotherapy or biologic therapy.
The standard immunotherapy drug for Bladder Cancer is a weakened bacterium called bacillus Calmette-Guerin. BCG is placed directly into the Bladder through a catheter. This is called intravesical therapy. BCG attaches to the inside lining of the Bladder and stimulates the immune system to destroy the tumor.
Radiation therapy
used after surgery to kill any remaining Cancer cells. Depending on the method of imparting radiation, it is categorized into:
- External-beam radiation therapy: This is the most common type of radiation treatment. In this radiation therapy given from a machine outside the body to send radiation towards the Cancer.
- Internal beam radiation therapy: If radiation therapy is given using implants, it is called internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. In this, a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters is placed directly into or near the Cancer

Bladder Cancer is highly treatable when diagnosed at an early stage when fortunately most diagnoses are made. However, Bladder Cancer has a high rate of recurrence. Hence, post-therapy patients are recommended to go for regular screening at least once a year.
01

In case of experiencing any of the mentioned symptoms or having a prior or familial history of Bladder Cancer, a physical examination by a specialist is highly recommended
02

Being aware of the symptoms and keeping a vigilant eye on the health conditions and any particular changes in the body behavior helps in discovering the disease at an early stage.
